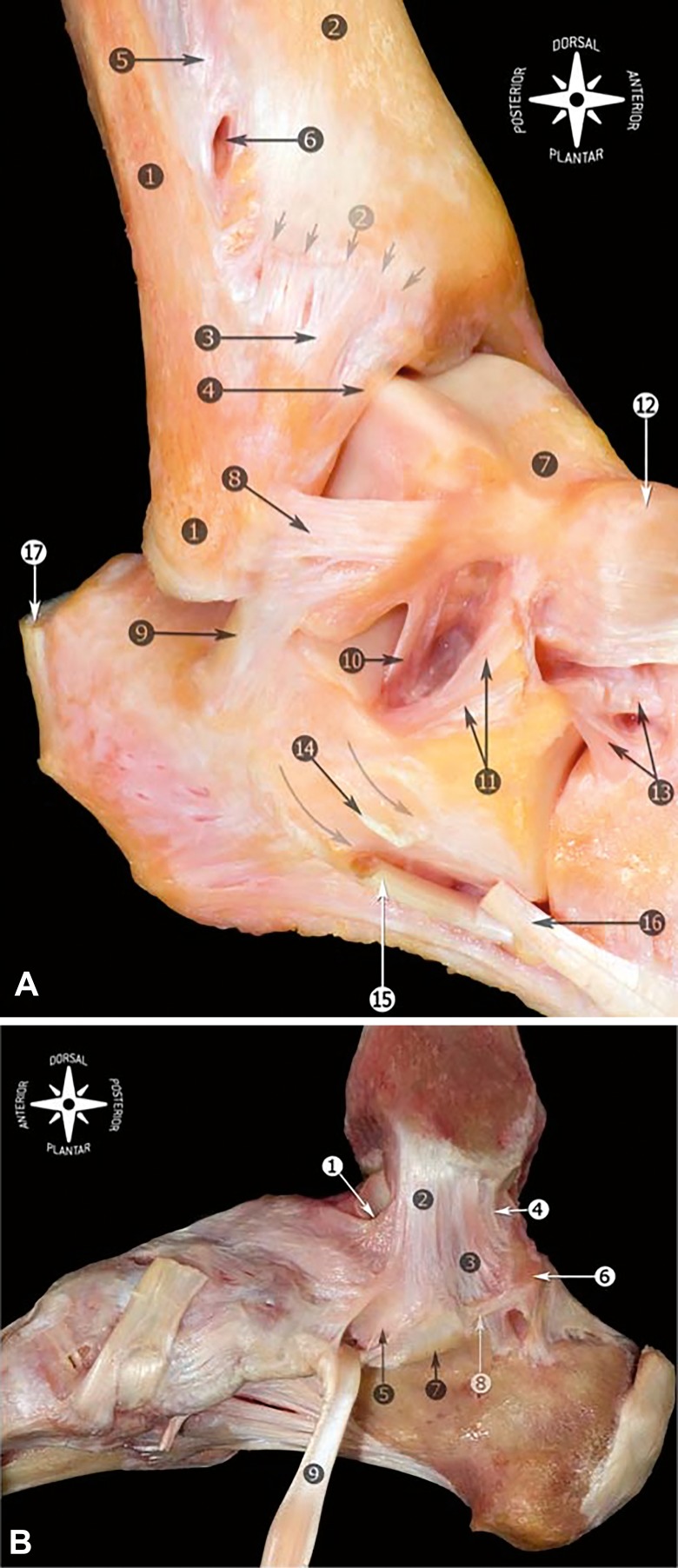
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the ankle ligaments. Right ankle. A, Fibula and tip of the fibula (1); tibia and anterior tubercle with arrows (2); anterior tibiofibular ligament (3); distal fascicle of the tibiofibular ligament (4); interosseous membrane (5); foramen for the perforating branch of the peroneal artery (6); talus (7); anterior talofibular ligament (8); calcaneofibular ligament (9); talocalcaneal interosseous ligament (10); inferior extensor retinaculum, cut (11); talonavicular ligament (12); bifurcate ligament (13); peroneal tubercle, arrows showing the peroneal tendons sulcus (14); peroneus longus tendon (15); peroneus brevis tendon (16); and calcaneal tendon (17). B, Medial view of the anatomic dissection of the main components of the medial collateral ligament. Tibionavicular ligament (1); tibiospring ligament (2); tibiocalcaneal ligament (3); deep posterior tibiotalar ligament (4); spring ligament complex, superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (5); medial talar process (6); sustentaculum tali (7); medial talocalcaneal ligament (8); and tibialis posterior tendon (9). Reprinted from Golanó P, Vega J, de Leeuw PA, Malagelada F, Manzanares MC, Götzens V, van Dijk CN. Anatomy of the ankle ligaments: a pictorial essay. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(4):944–956. Available through Open Access.