Figure 1.
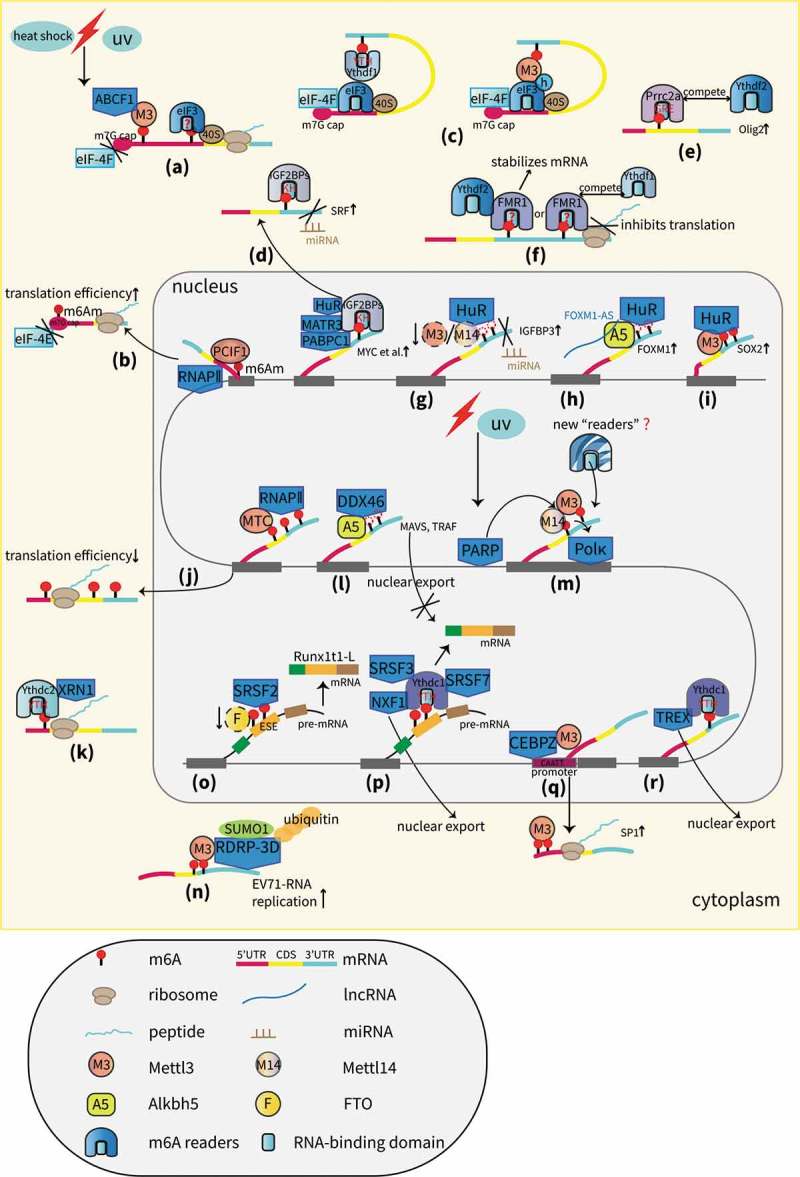
A proposed model of RBPs in the m6A field. (a) Cap-independent translation is mediated by m6A and requires the eIF3 (reader protein), ABCF1, and Mettl3 proteins that bind to internal m6A residues but not to the m7G cap [33,34]. (b) PCIF1 interacts with RNAPII and regulates the N6-methylation of m6Am, which promotes the translation of capped mRNAs [36]. (c) Ythdf1 or Mettl3 promotes translation with the help of eIF3 and mRNA circularization [37,38]. (d) IGF2BPs promote the translation of m6A-mRNAs either by stabilizing targets, such as MYC with the aid of mRNA stabilizers, including HuR, MATR3 and PABPC1 or by antagonizing miRNA-directed mRNA repression [39,45]. (e) Prrc2a stabilizes olig2 mRNA by binding to m6A sites in the CDS and competes with Ythdf2 to regulate RNA stability [46]. (f) FMR1 stabilizes m6A mRNAs by interacting with Ythdf2 or inhibits translation by competing with Ythdf1 [48,49]. (g) HuR stabilizes IGFBP3 mRNA by preventing miRNA targeting [53]. (h) HuR promotes the stability of the demethylated mRNA of FOXM1, which is mediated by Alkbh5, and the cooperation between Alkbh5 and FOXM1-AS.[105] (i) Mettl3 stabilizes the mRNA of SOX2 by recruiting HuR [57]. (j) Slow or paused RNAPII dynamics facilitate MTC binding and m6A deposition, leading to reduced translation efficiency [59]. (k) Ythdc2 stabilizes m6A-mRNAs by interacting with XRN1 [60]. (l) Alkbh5 inhibits the nuclear export of several antiviral transcripts by recruiting DDX46 [62]. (m) Mettl3, recruited by PARP, promotes m6A deposition and subsequent Pol κ binding accompanied by Mettl14, leading to cell survival from DDR [9]. (n) Mettl3 interacts with RdRp-3D and regulates the sumoylation and ubiquitination of RdRp-3D that can promote viral replication [63]. (o) The loss of FTO promotes m6A deposition and the SRSF2 binding ability, leading to the increased inclusion of target exons [69]. (p) Ythdc1 recruits SRSF3 and SRSF7 to promote exon inclusion; Ythdc1 recruits SRSF3 and NXF1 to promote nuclear export [7,70]. (q) CEBPZ recruits Mettl3 to gene promoter regions to augment their translation [73]. (r) TREX interacts with Ythdc1 to promote nuclear export [74].
