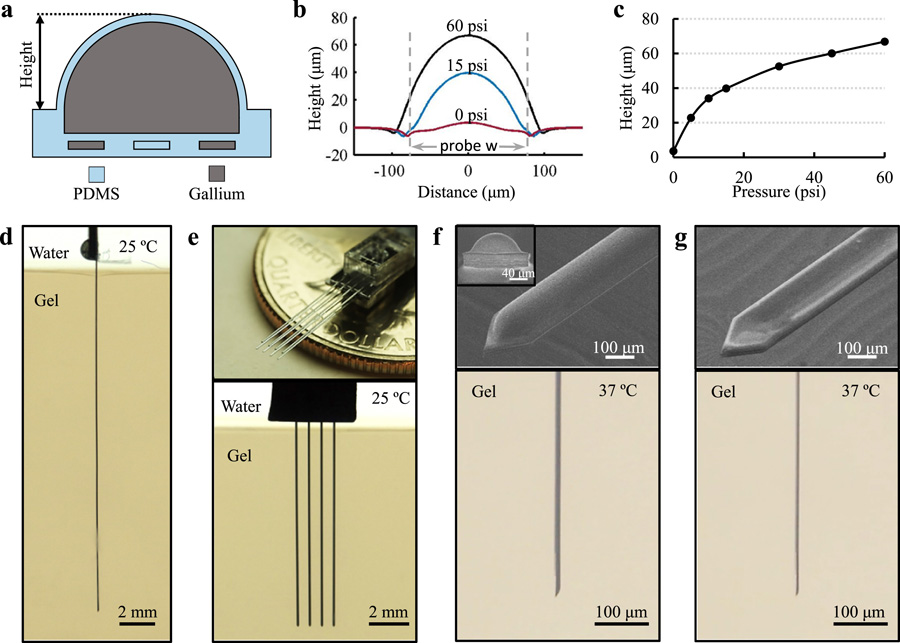
Fig. 2. Characterization of Probe Tunable Stiffness and Implantation Capability in Brain Phantoms.
(a) Schematic cross-sectional view of an inflated probe. (b,c) Characterization of the probe shank swelling with respect to different Ga filling pressure. Dashed lines represent the boundaries of the probe (144 μm-wide). The slightly longer distance under 60 psi is a measurement artifact due to steep edge of the largely deformed probe and the cone shape of the profilometer’s stylus. (d) Demonstration of a 2 cm-long ULTS probe implanted in a brain phantom (0.6% agarose gel) at room temperature, with a Ga injection pressure of 60 psi to achieve maximum stiffness. (e) Top, picture of a 4 × 2 probe array by stacking two 4-shank probes. Bottom, insertion of a 1 cm-long, 4-shank probe in a brain phantom. (f) ULTS probe in the “inflated” state with 15 psi injection pressure. Top, SEM ‘bird’s-eye’ view. Inset, front view showing a shank swelling height of 40 μm, scale bar, 40 μm. Bottom, side-view of an inflated probe implanted in a brain phantom. (g) ULTS probe in the “deflated” state. Top, SEM ‘bird’s eye’ view. Bottom, side-view of a probe in a brain phantom deflated by active suction of Ga.