Figure 6.
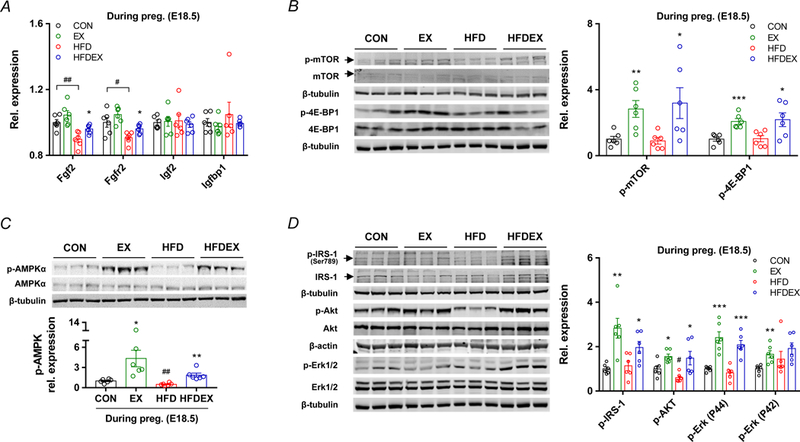
Maternal exercise training activates AMPK/mTORC1/insulin signaling in the placenta of HFD mice with exercise. A, mRNA levels of growth factors in CON or HFD mice with/without exercise mice (n = 6 per group). Expression was normalized by ΔCt values. B, cropped western blots of mTOR phosphorylation and 4E-BP1 phosphorylation in the placenta (the total mTOR or total 4E-BP1 were used as the reference). C, cropped western blots of AMPK phosphorylation in the placenta (the total AMPK was used as the reference). D, cropped western blots of IRS-1 phosphorylation, and Akt phosphorylation, and Erk½ phosphorylation in the placenta (the total IRS-1, total Akt, and total Erk½ were used as the references). Data are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. n = 6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 in CON vs. EX or HFD vs. HFDEX; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.001 in CON vs. HFD by two-tailed Student’s t-test (A-D).
