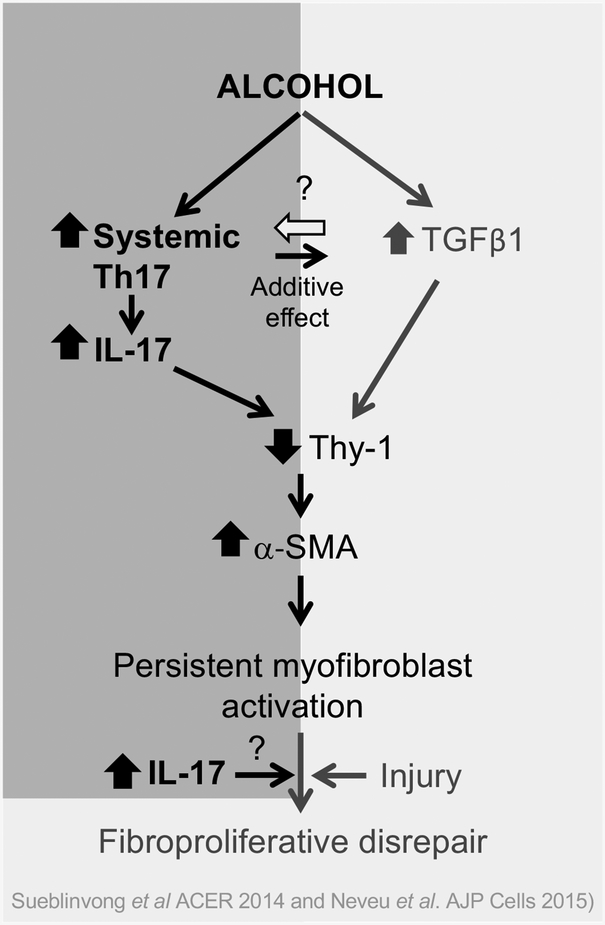
Figure 10. Hypothesis schematic showing the effects of IL-17 on myofibroblast development in chronic alcohol ingestion.
In the current study, we showed that in the otherwise healthy animals, chronic alcohol ingestion increased systemic Th17 immune response. Acute injury caused a persistent increase in IL-17 in the lung. Alcohol, IL-17, and TGFβ1 independently inhibited Thy-1 expression by lung fibroblasts and IL-17 and TGFβ1 additively decreased Thy-1 expression leading to myofibroblast differentiation. We believe this sequence of events is one of the mechanisms by which alcohol induces fibroproliferative disrepair following acute lung injury.