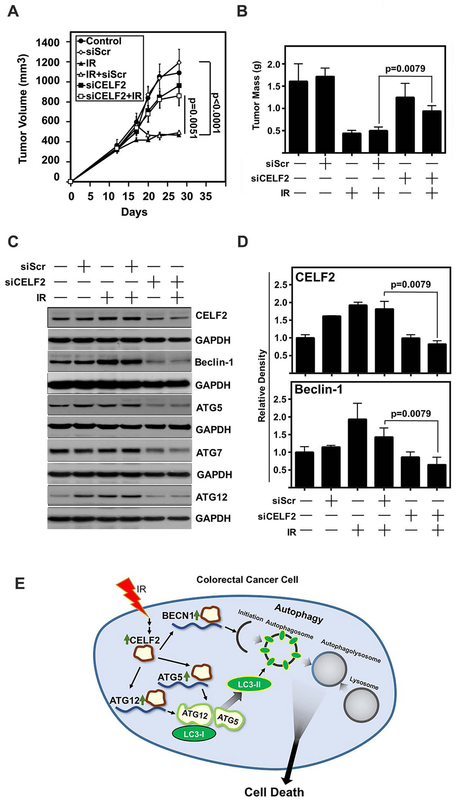
Fig. 6. CELF2 is required for IR-mediated tumor growth suppression in vivo.
(A) Tumor volume of HCT116 xenograft tumors in nude mice. Mice were treated with IR (2 Gy) on days 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17. Scrambled (Scr) or CELF2 siRNA was delivered in DOPC lipid capsules on days 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17. n=10 tumors in control, siScr, siScr + IR, and siCELF2 groups, n=12 tumors in IR alone and siCELF2 + IR. Tumor volume determined by vernier calipers and error bars represent ± SEM.
(B) Tumor weight of excised tumors at the conclusion of the experiment (n=5 per group). Graph depicts mean weight and error bars represent ± SEM.
(C) Immunoblot of excised representative tumors demonstrates increase of CELF2, Beclin-1, Atg5 and Atg12 in IR treated tumors, with a reduction in siCELF2 treated tumors.
(D) Cumulative results of densitometric analysis of CELF2 and Beclin-1 immunoblots of excised HCT116 xenografts relative to GAPDH as loading control. N=5 per group.
(E) Schematic representation of IR induction of CELF2 and subsequent initiation of autophagic cell death.