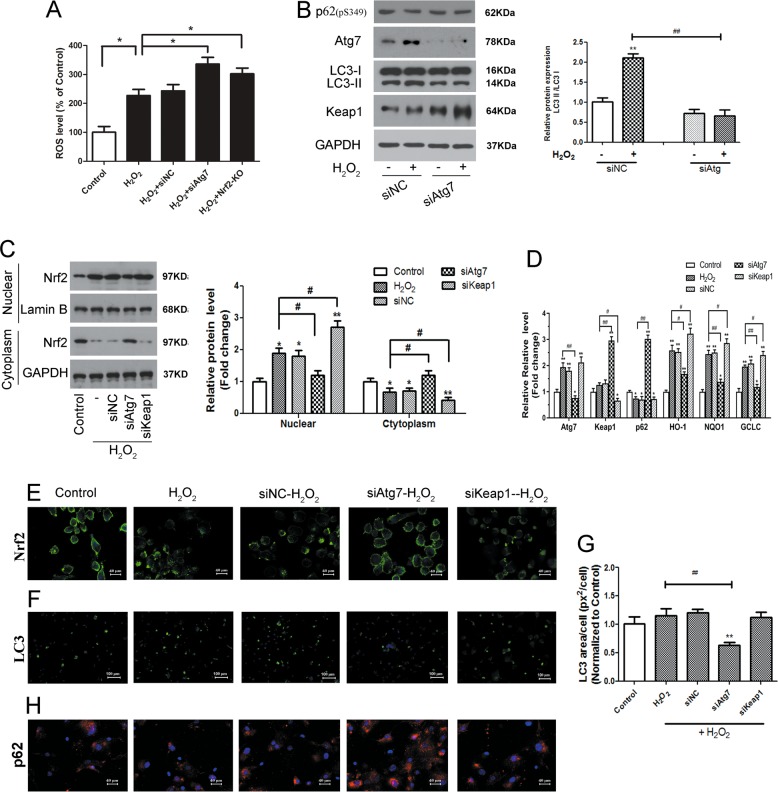
Fig. 5. H2O2-induced oxidative stress was increased in autophagy-deficient cells via Atg7 and Keap1–Nrf2–p62 autophagy pathway.
a Autophagy-deficient cells have higher levels of ROS. Knockout of Nrf2 and autophagy impaired by Atg7 knockdown increased the elevated ROS level in NP cells stimulated with 400 μM H2O2 for 2 h. *p < 0.05. b NP cells were transfected with Atg7 siRNA or control siRNA 24 h before H2O2 treatment. Cells were treated with 400 µM of H2O2 for 2 h. Level of p62(pS349), Atg7 and LC3-II and Keap1 degradation was analyzed by western blotting. Atg7 knockdown blocked the accumulation of LC3-II and inhibited Keap1 degradation induced by H2O2 exposure. ##, **p < 0.01; * vs. siNC- H2O2(−), # vs. siNC- H2O2(+). c NP cells transfected with Atg7 siRNA, Keap1 siRNA, control siRNA or WT NP cells were treated with H2O2 (400 μM) for 2 h, and then the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were isolated for western blotting. Lamin B and GAPDH were used as markers for nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively. Note that Atg7 siRNA inhibited while Keap1 siRNA promoted the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 induced by H2O2. *, #p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; * vs. Control, # vs. H2O2 induced cells. d NP cells transfected with Atg7 siRNA, Keap1 siRNA, control siRNA or WT NP cells were treated with H2O2 (400 μM) for 2 h, and the mRNA expression of Atg7, Keap1, p62, HO-1, NQO1 and GCLC was measured by qPCR. e Confocal microscopy confirmed the nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Green, Nrf2; Blue, DAPI. f Fluorescent microscopy for the formation (Green, LC3; Blue, DAPI) and distribution of LC3. *, #p < 0.05; ##, **p < 0.01; * vs. Control, # vs. H2O2 induced cells. g LC3 punctate was quantified as LC3 area per cell (px2/cell) normal to control. ##, **p < 0.01; * vs. Control, # vs. H2O2 induced cells. h Confocal microscopy confirmed the translocation of p62 Red, p62; Blue, DAPI. Atg7 siRNA reduced while Keap1 siRNA increased LC3 puncta which was contrary to p62 under H2O2-induced oxidative stress