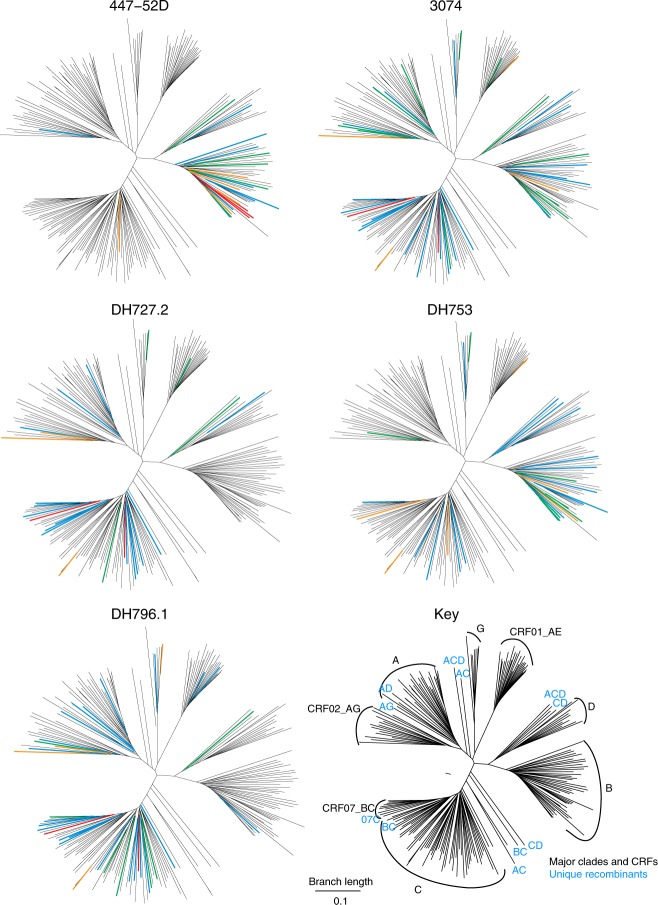
Fig. 2.
HIV-1 phylogenetic trees indicate clade-specific antibody neutralization patterns. These phylogenetic trees are based on the 208 pseudovirus panel, to allow direct visual comparisons of the vaccine-elicited antibodies with 447-52D. The HIV-1 envelope gp160 sequences were used to construct maximum likelihood trees, each HIV-1 clade is indicated in the key. Circulating recombinant forms (CRFs)30 are indicated when they are major epidemic lineages: CRF02 is an AG recombinant that is A-like in Env and common in West Africa, CRF01 is an AE recombinant that is E-like in Env and common in southeast Asia, and CRF07 is a BC recombinant that is C-like in Env that is common in China. Unique recombinants are indicated in the dendrogram with blue letters indicating the parental virus clades. Neutralization IC50 titers for HIV-1 infection of TZM-bl cells are shown for two HIV-1 antibodies from natural infection (447-52D and 3074; top row) and vaccine-induced antibodies (DH727.2, DH753, DH796.1; bottom row). Neutralization potency is color-coded based on IC50 in µg mL‒1 as red 0.001–0.01, orange 0.01–0.1, green 0.1–1, blue 1–50 and black > 50. Of note is both the clade specificity of these antibodies, and the recurrence of the same subsets of viruses being sensitive within each clade. Source data are provided as a Source Data file