Figure 2.
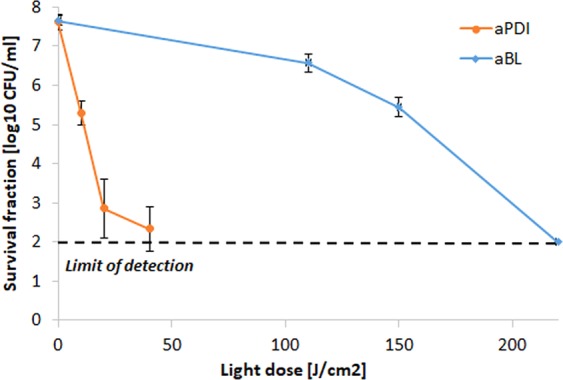
Influence of aPDI and aBL on S. aureus strain. Microbial overnight cultures were (5 × 107 CFU/ml) were treated with 1 µM RB and exposed to different light doses up to 40 J/cm2 (λmax 515 nm). The aBL samples were irradiated with different light doses of blue light up to 220 J/cm2 (λmax 411 nm). After illumination, samples were serially diluted, streaked horizontally, incubated at 37 °C for 16–20 h, and then colonies were counted. Control groups included cells that were not treated with PSs or light. For the purpose of this study, lethal doses of aPDI/aBL were defined as the treatment that resulted in an approximately ≥3 log10 reduction in CFU, and sub-lethal doses were defined as a 2 log10 reduction in CFU. The detection limit was 100 CFU/ml. The values are the means of three separate experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD).
