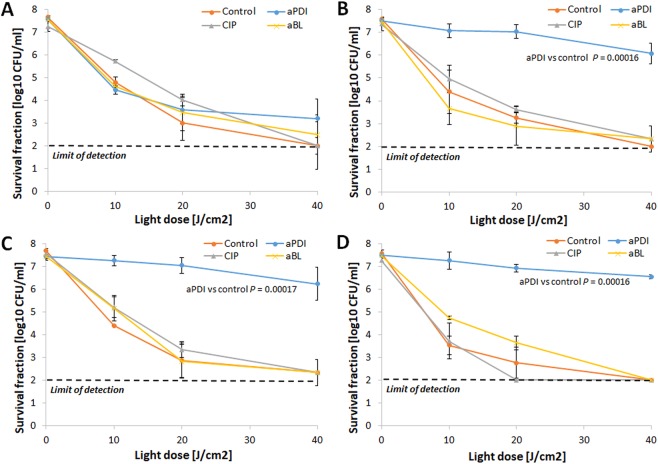
Figure 3.
aPDI tolerance development upon sub-lethal RB-aPDI treatment. Overnight JE2 cultures (5 × 107 CFU/ml) were incubated with 0.1 μM RB and illuminated with 515 nm light at a dose of 10J/cm2. Following exposure, 10 μL aliquots of the treated samples were taken to determine the survival rate. The rest of the sample was centrifuged and washed with PBS. Fifty microliters of the samples was transferred into fresh TSB medium (5 mL) to re-grow overnight. The next day, the treatment was repeated under the same conditions. The cycle of exposure - regrowth - exposure was repeated 15 times. Control groups included cells that were not treated with PSs or light but were treated with a sub-MIC dose of CIP (0.25 μg/ml) (regrowth overnight, 15 passages). The susceptibility of S. aureus to RB-aPDI was investigated upon 1 (panel A), 5 (panel B), 10 (panel C) and 15 (panel D) cycles of sub-lethal RB-aPDI/aBL or CIP (½ MIC). The detection limit was 100 CFU/ml. The values are the means of three separate experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD).