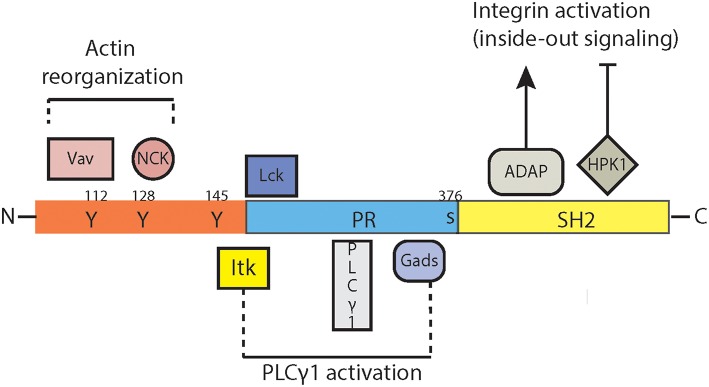
Figure 2.
Signaling domains of slp-76. SLP76 (SRC homology 2 (SH2)-domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa) contains inducibly phosphorylated tyrosines in the amino (N) terminus, a central proline-rich (PR-) domain and a carboxy (C)-terminal SH2 domain. The N-terminal acidic domain binds to the SH2 domains of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav, the adaptor protein Nck and the Tec-family kinase Itk. The subsequent signaling pathways influence predominantly the reorganization of actin. This domain of slp-76 interacts also with the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K) which interfere with multiple cellular functions such as proliferation, differentiation and survival. The central proline-rich domain of slp-76 interacts with the phospholipase PLCγ-1 and the adaptor molecule GADS (Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc). The C-terminal SH2 domain of slp-76 binds to the serine-threonine kinase HPK-1 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1) and to the adhesion and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein (ADAP), two molecule associated with the formation of the immunological synapse, integrin activation/expression and inside-out and outside-in signaling cascades. ADAP, adhesion- and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein; GADS, GRB2-related adaptor protein; GRB2, growth-factor-receptor-bound protein 2; HPK1, hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1; ITK, interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase; Lck, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; NCK, non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase; PLCγ1, phospholipase Cgamma1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PR, proline-rich; Vav, guanine nucleotide exchange factor.