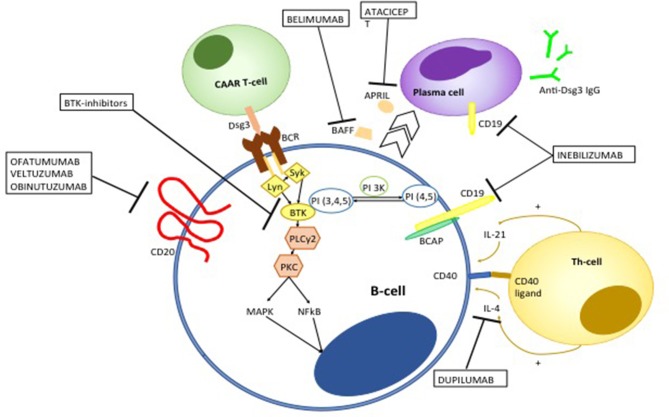
Figure 9.
Emerging therapies targeting auto-reactive B and T-cells in pemphigus. Ofatumumab, veltuzumab, and obinutuzumab are fully human or humanized monoclonal antibodies targeting CD20. Ofatumumab and veltuzumab are class I anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, with a higher capacity of binding CD20 and inducing complement-dependent cytotoxicity compared to RTX. Obinutuzumab is a class II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, that has an increased affinity to the FcγIII receptor, resulting in a more potent antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. Bruton kinase (BTK) inhibitors interfere with B cell activation. BCR signaling induces migration of BTK from the cytosol to the cell membrane, though the interaction with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosfate generated by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). BTK is activated by Lyn and Syk and then actives downstream molecules including phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCγ2) and Protein kinase C. The latter in turns activate different pro-inflammatory pathways including mitogen associated protein kinases (MAPK) and Nuclear Factor k B (NFkB). Chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR)-T-cells are engineered T-lymphocytes which express Dsg3 ectodomain, which allows recognition and subsequent killing of B-cells targeting Dsg3. Belimumab and atacicept target B-cell derived B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), respectively, which promote differentiation toward autoantibody-producing plasma cells. Inebilizumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD19 which is not only expressed on B cells but also plasma cells. Dupilumamb is a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin (IL-4), which is one the main cytokine produced by T helper 2 cells and T follicular helper cell which induces autoantibody production by autoreactive B-cells.