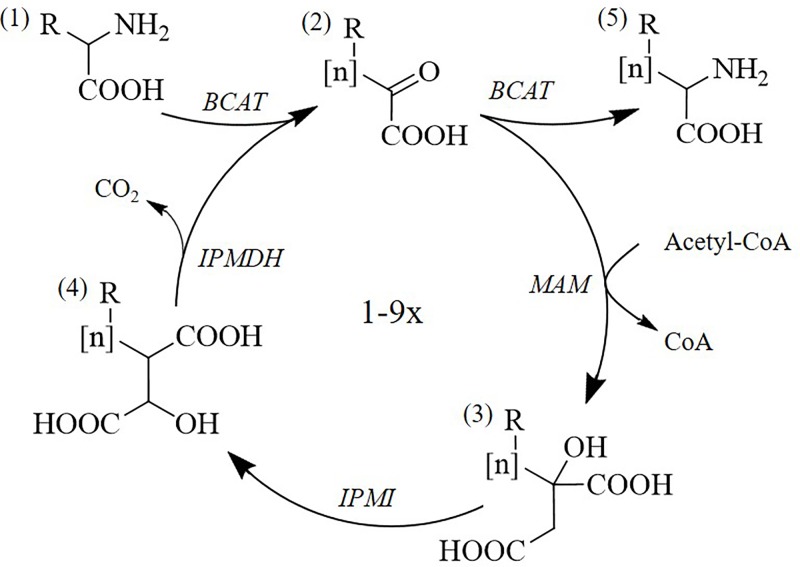
Figure 1. Schematic view of the chain elongation pathway in glucosinolate biosynthesis.
The first step is deamination by a branched-chain aminotransferase (BCAT), followed by a three-step cycle: condensation by a MAM, isomerisation by an isopropylmalate isomerase (IPMI) and oxidative decarboxylation by an isopropylmalate dehydrogenase (IPMDH). At this point the intermediate will either go through another cycle or exit by transamination by a BCAT. The pathway intermediates are (1) amino acid, (2) 2-oxo acid, (3) 2-alkylmalic acid, (4) 3-alkylmalic acid and (5) chain-elongated amino acid.