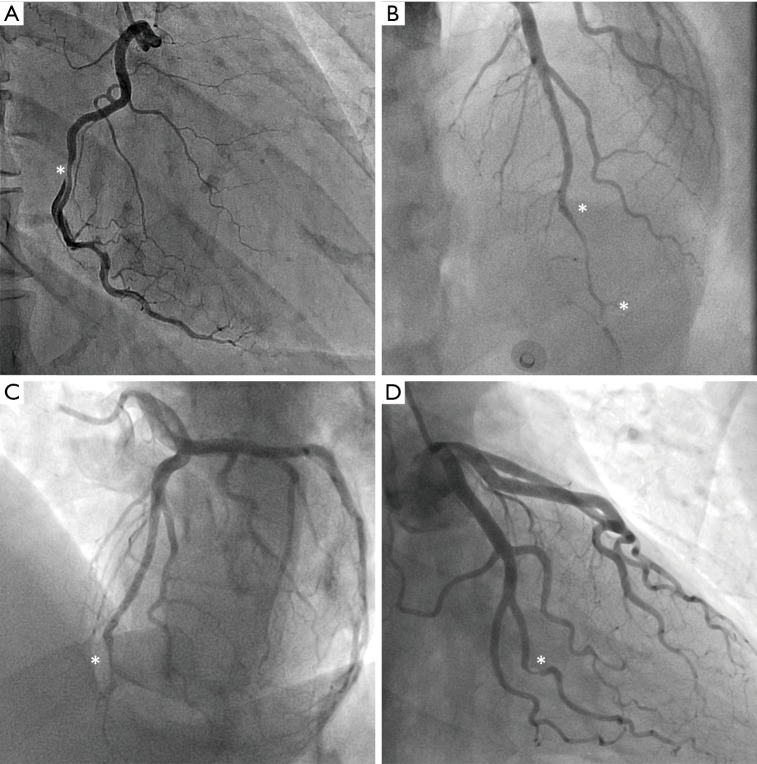
Figure 2.
Angiographic classification of SCAD. (A) shows Type 1 SCAD of the right coronary artery, characterised by a double lumen illustrated by contrast hold-up. (B) and (C) show Type 2 SCAD of the left anterior descending artery, which involves abrupt narrowing of the coronary artery with a diffuse tubular stenosis, either for a section of the artery in Type 2a (B), or to the distal end of the artery in Type 2b (C). (D) shows Type 3 SCAD of the second obtuse marginal branch of the left circumflex artery, mimicking atherosclerotic disease. In this case, SCAD was confirmed by optical coherence tomography. Asterisks denote the locations of dissection. SCAD, spontaneous coronary artery dissection.