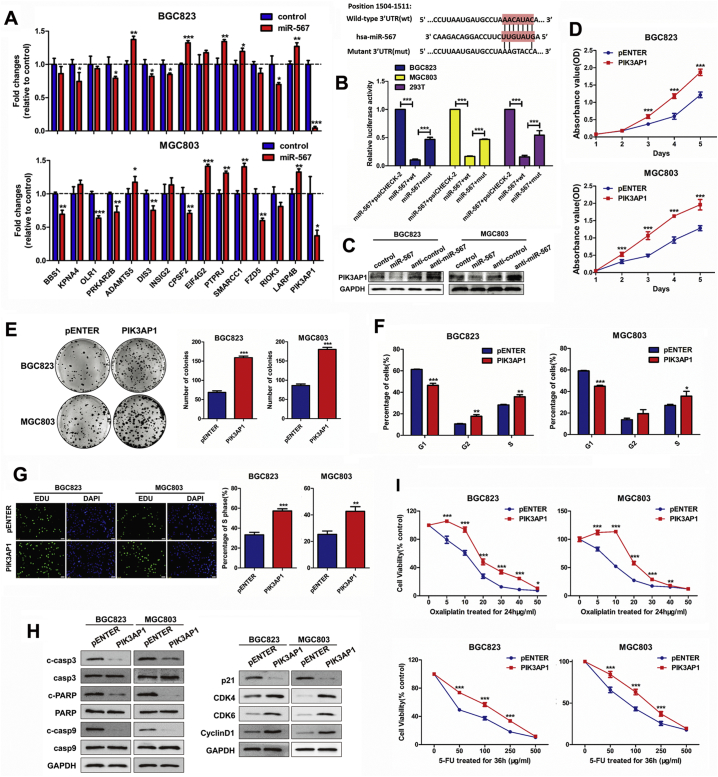
Fig. 3.
PIK3AP1 is the direct target of miR-567 and promotes GC cell proliferation and increases drug sensitivity. (A) Real-time PCR analysis were performed to detect the mRNA expression of candidate genes in MGC803 and BGC823 cells transfected with miR-567 mimic, Student's t-test, mean ± SD. (B) miR-567 and its putative binding sequences in the 3′UTR of PIK3AP1. A mutation was generated in the complementary site that bound to the seed region of miR-567. Luciferase reporter assay was used to determine miR-567 direct targeting the PIK3AP1 3′UTR, Student's t-test, mean ± SD, ***P < .001. (B) Western blot analysis were performed to detect the protein expression of PIK3AP1 in MGC803 and BGC823 cells, both transfected with miR-567 mimic or anti-miR-567. CCK-8 assay (C), colony formation assay (D), FACS assays (E) and EdU incorporation assays (F) of GC cells were performed after transfected with PIK3AP1 or pENTER vector, Student's t-test, mean ± SD, *P < .05; **P < .01. (H) Western blot experiments were used to analyse the expression of pro-apoptosis proteins, cell cycle maker and related proteins in PI3K/AKT pathway after miR-567 knockdown and overexpression in MGC803 and BGC823 cells. (I) Dose-response curves of MGC803 and BGC823 treated with 5-FU for 36 h or oxaliplatin for 24 h, the cells were previously transfected with PIK3AP1 and pENTER. Parametric generalized linear model with random effects, Student's t-test, mean ± SD, *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.