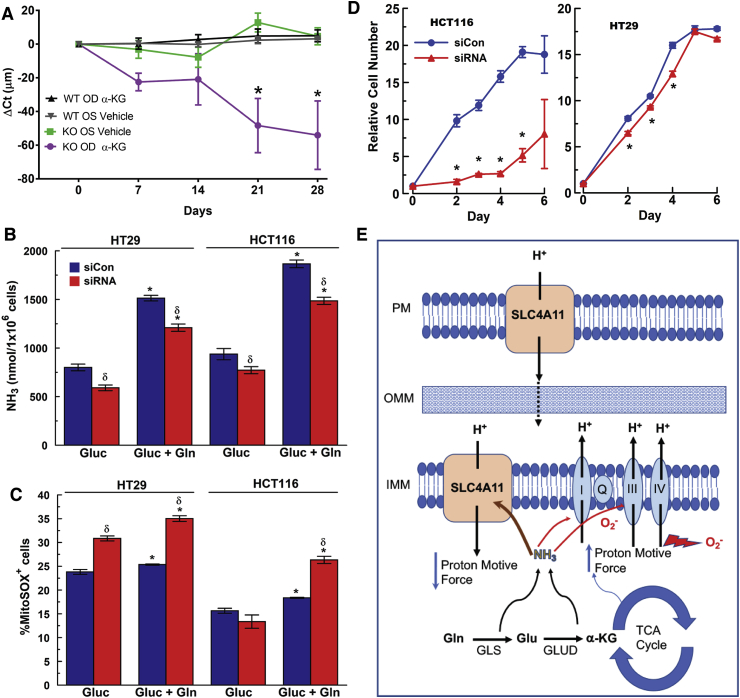
Fig. 9.
Rescue of Slc4a11 KO Mouse, SLC4A11 knockdown in Colon Carcinoma, and Model for Activity. (A) Change in Corneal Thickness (ΔCt) in three WT and three KO mice receiving one drop of 50 mM dimethyl-αKG three times per day over 28 days. Vehicle was Lacripure saline solution osmotically matched with sucrose. *p < 0.05 significantly reduced compared to vehicle. (B) Effect of transient siRNA knockdown of SLC4A11 on ammonia production and (C) MitoROS in HT29 and HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. Cells were incubated in assay media with 2 mM Glutamine for 24 h. Media was collected for ammonia assay and cells were stained for 20 min with 2.5 μM MitoSOX 37 °C, followed by one wash with HBSS and analyzed by flow cytometry into MitoSOX+ or MitoSOX− populations. n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs Gluc, same siRNA treatment, δ: p < 0.05 vs Negative siRNA. (D) Effect of transient siRNA knockdown of SLC4A11 on HT29 and HCT116 proliferation, n = 3, *p < 0.05, ±SD. (E) Model for SLC4A11 function at plasma membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane. Glutamine derived αKG accelerates the TCA cycle and energizes the ETC, which increases the proton motive force and together with [NH3], increase the production of ROS. Mild uncoupling from NH3 activated SLC4A11 reduces the proton motive force, lowering ROS production, protecting mitochondria, and facilitating glutamine catabolism.