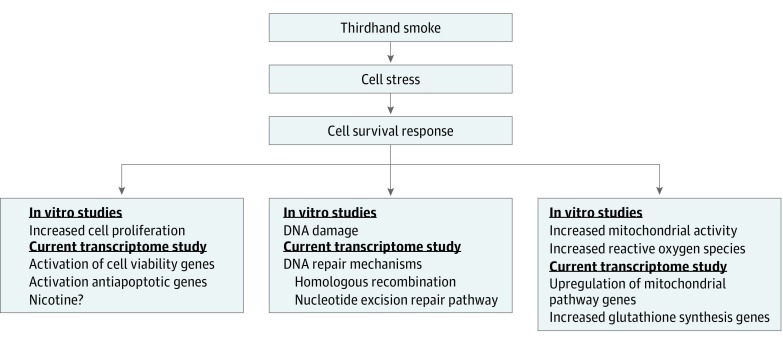
Figure 3. Schematic Diagram Summarizing the Responses of Human Nasal Epithelium to Thirdhand Smoke.
Thirdhand smoke induced cellular stress leading to activation of cell survival responses, including activation of DNA repair pathways, increased cell proliferation, and increased mitochondrial activity in the human nasal epithelium. Previous in vitro studies have shown similar results in which thirdhand smoke causes DNA damage,9,10 increased cell proliferation,11,43 increased mitochondria activity,12 and increased reactive oxygen species.12