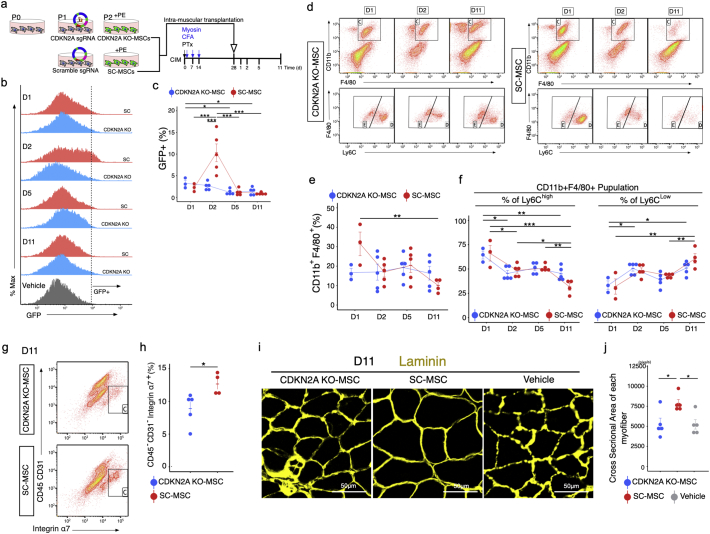
Fig. 6.
CDKN2A-KO MSCs exert reduced therapeutic effects in CIM. (a) Procedure for generation of CDKN2A KO-MSCs and protocol for MSC treatment. (b and c) Flow cytometry analysis of GFP+ cells of triceps surae in CIM 1, 2, 5, and 11 days after transplantation of GFP-labelled MSCs (b), and percentage of GFP+ cells (c). (d–f) Flow cytometry analysis of CD11b, F4/80, and Ly6C (d); quantification following MSC transplantation: percentage of CD11b + F4/80+ total macrophages (e), CD11b + F4/80+ Ly6Chi pro-inflammatory macrophages (f), and CD11b + F4/80+ Ly6Clow pro-fibrotic macrophages (f) (n = 3–5 per group). (g and h) Flow cytometry analysis of CD45, CD31, and α7-integrin (g), and quantification 11 days after MSC transplantation (h) (n = 3–4 per group). (i and j) Representative image of laminin-immunostained triceps surae 11 days after MSC transplantation (i), and quantification of the cross-sectional area of each myofiber (j). Quantitative data are shown as means ± SEM (dot plot). P-values were determined by two-tailed Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA adjusted by Tukey's method. (*P < .05, **P < .001).