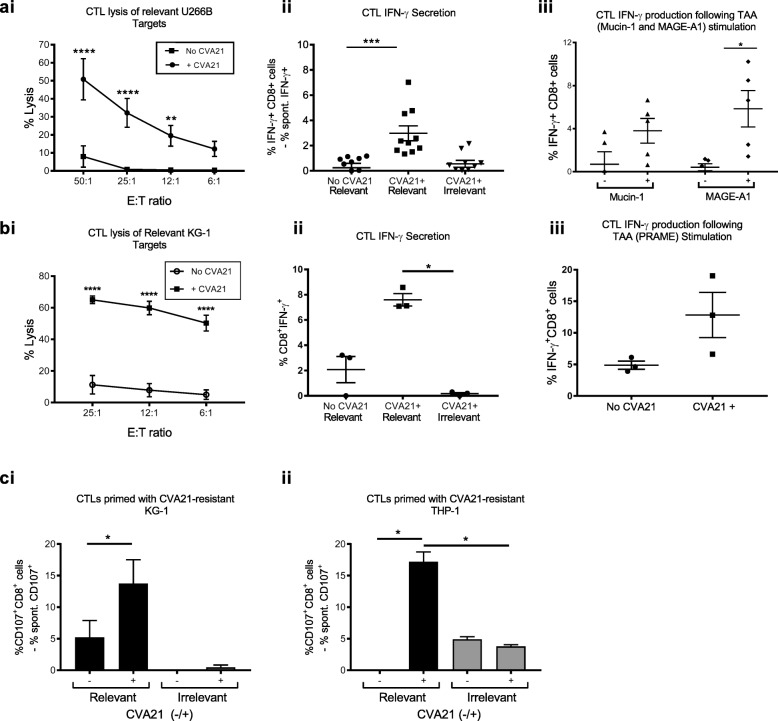
Fig. 4.
CVA21 can prime tumor-specific CTL. a. and b: CVA21-sensitive U266B MM (a) and ICAM-1/KG-1 (b) cell targets were used. Tumor cells were pre-treated with CVA21 (0.1 pfu/cell) for 24 h, then loaded onto mDC prior to being co-cultured with autologous PBMC and one round of re-stimulation. a. and bi. CTLs primed in the presence or absence of CVA21 were co-cultured with 51Cr-labelled relevant targets (U266B and ICAM-1/KG-1 cells, respectively) at different effector:target ratios for 4 h. The percent cell lysis was determined using 51Cr release (n = 6). a. and bii. CTL intracellular IFN-γ production following a 5 h co-culture with relevant (U266B or ICAM-1/KG-1, respectively) or irrelevant (ICAM-1/KG-1 or Raji, respectively) targets (n = 3). a. and biii. Intracellular IFN-γ production following a 5 h co-culture with autologous CD14+ cells loaded with appropriate peptide pools (Mucin-1 and MAGE-A1; U266B CTLs, and PRAME; ICAM-1/KG-1 primed CTLs). c. CTL priming with CVA21-resistant cells (parental-KG-1 (i) and THP-1 (ii)). The percentage of tumor specific CTLs (CD3+CD8+) was determined using CD107a/b degranulation after a 5 h co-culture with relevant (KG-1; n = 3 or THP-1; n = 2) or irrelevant (Raji) cell targets. Spontaneous CD107 expression was subtracted from the values shown. Error bars indicate SEM. *denotes statistical significance