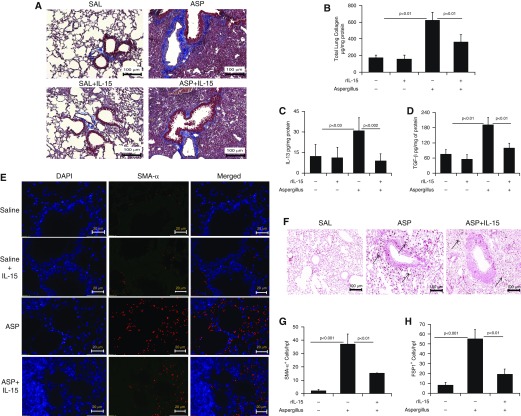
Figure 2.
Consequences of rIL-15 pretreatment in Aspergillus-induced bronchial fibrosis in mice. (A) Representative light-microscopy photomicrographs of lung sections with Masson’s trichrome staining show perivascular and peribronchiolar collagen accumulation after 3 weeks of saline or Aspergillus challenge in mice treated with and without rIL-15. (B) Total collagen expression in saline- and rIL-15–treated, Aspergillus-challenged mice. ELISA results for profibrotic IL-13 and TGF-β1 expression in saline- and rIL-15–treated, Aspergillus-challenged mice are shown. (C and D) Immunofluorescence staining revealed α-SMA+ cells in Aspergillus- and rIL-15–treated, Aspergillus-challenged mice. (E) Very few eosinophils are seen in the saline-treated (for 3 wk) mice. (F) Arrows indicated FSP1+ cell expression in Aspergillus and rIL-15–treated Aspergillus-challenged mice. Quantitation of α-SMA+ and FSP1+ cells is shown in saline-, (G and H) Aspergillus-, and rIL-15–treated Aspergillus-challenged mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 12 mice/group. Scale bars: 100 μm and 20 μm. ASP = Aspergillus; FSP1 = fibroblast-specific protein 1; rIL-15 = recombinant IL-15; SAL = saline.