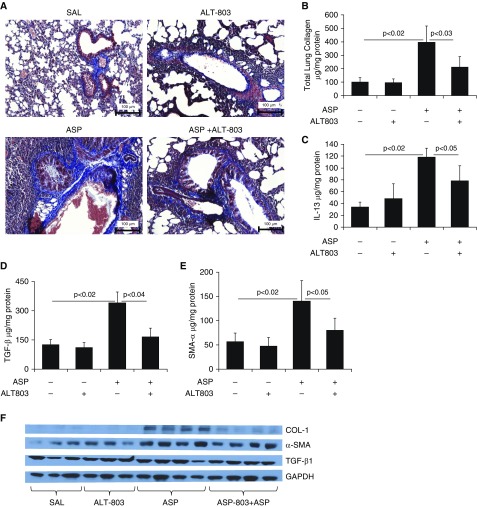
Figure 7.
Reduction in lung collagen and the levels of profibrotic cytokines in response to pretreatment with the human IL-15 agonist ALT-803 in the lungs of Aspergillus-challenged mice. The potential of a human IL-15 agonist as a therapeutic agent was examined using an allergen-induced lung fibrosis model. (A) A highly significant reduction in collagen accumulation is shown in response to ALT-803 treatment (regimen of 5 μg on alternate days for 3 wk) in Aspergillus-challenged mice compared with saline-treated, Aspergillus-challenged mice. (B–E) Total lung collagen (B) and the profibrotic cytokines IL-13 (C), TGF-β1 (D), and α-SMA (E) in saline- and ALT-803–treated saline or Aspergillus-challenged mice are shown. (F and G) Western blot analysis showed that ALT-803 treatment downregulated Aspergillus-induced levels of profibrotic cytokines (collagen I, TGF-β1, and α-SMA) in mice (F), and this was further confirmed by GAPDH-normalized densitometry of collagen I, TGF-β1, and α-SMA (G). Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 12 mice/group in each group, except for the Western blot analysis. Scale bars: 100 μm.