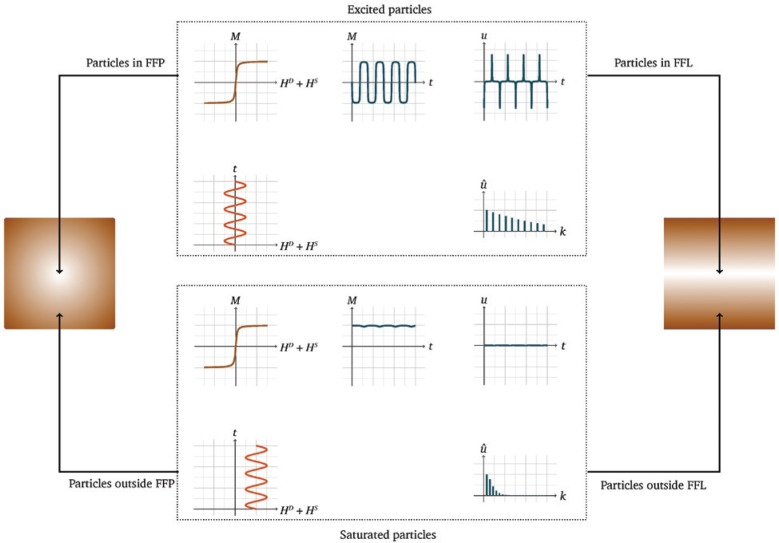
Figure 1:
The signal encoding principle in MPI is based on the excitation of MNPs by an oscillating magnetic field called drive field HD(t).
Based on a modulation of the drive field by the particles’ non-linear magnetization curve, a characteristic receive signal u(t) can be induced. As shown by the frequency spectrum û(t) of such a voltage signal, the modulation of HD(t) causes the generation of higher harmonics of the applied frequency. The principle for spatial encoding in MPI is based on the application of a selection field HS(i). All MNPs outside the area of the FFP or FFL or rather in a close vicinity to it remain in saturation, and thus do not contribute to the particle signal.