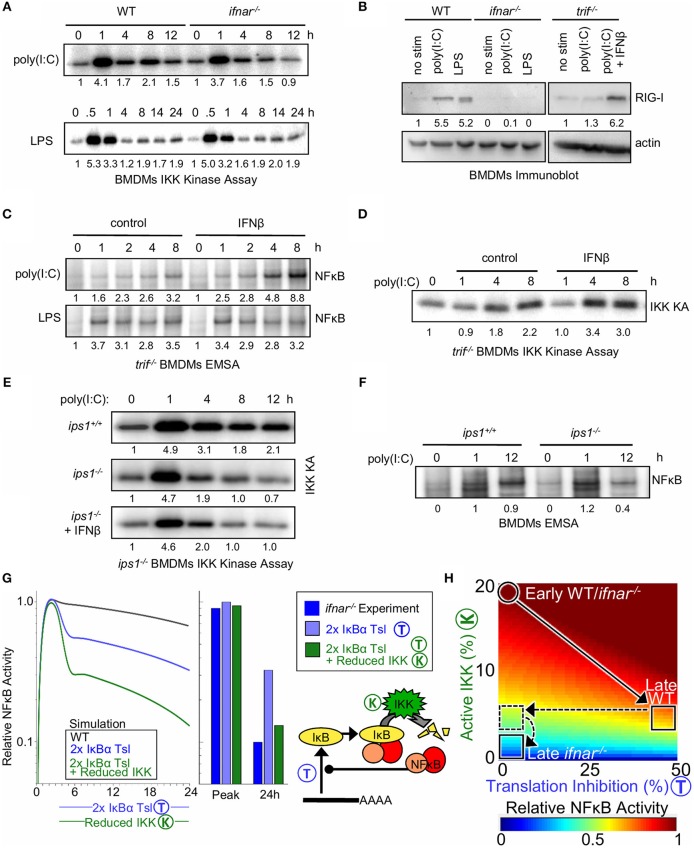
Figure 4.
Type I interferon potentiates late NFκB activation by poly(I:C) by decreasing IκB translation and increasing bound IκB degradation via elevated RigI expression. (A) Immunoprecipitation kinase assay (kinase A) of IKK activity in WT and ifnar−/− BMDMs in response to poly(I:C) and LPS. (B) Immunoblot of RIG-I expression after 8 h of poly(I:C) or LPS treatment in WT, ifnar−/− and trif−/− BMDMs; and rescue of trif−/− cells with IFNβ. (C) EMSAs of NFκB activation by poly(I:C) and LPS in trif−/− BMDMs with and without IFNβ co-treatment. (D) IKK activity in WT and ips−/− BMDMs exposed to poly(I:C) and in ips−/− cells with co-treatment with IFNβ. (E) IKK activity in trif−/− BMDMs with and without IFNβ co-treatment. (F) EMSAs of NFκB activation by poly(I:C) in ips1+/+ and ips1−/− BMDMs. (A–D) show a dataset representative of at least three biological replicates, and (E,F) show a representative of two biological replicates (we gratefully acknowledge Zhijian James Chen for ips1−/− bone marrow). Quantitations are relative to basal or peak activity, which is set to 1. (G) (Left) Simulated NFκB timecourse in response to IKK activation representative of poly(I:C) stimulation, with a 2-fold increase in IκBα translation (blue) or with both IκBα translation inhibition and 50% IKK activity reduction as seen in ifnar−/− (green). (Right) Bar graph of NFκB activity at the peak and 24 h time point as quantified from simulations and experiments (Figure 2A). (H) Heatmap of NFκB activity calculated using SiMoN for 50 increasing IKK activity values and 50 increasing degrees of translation inhibition (2,500 total points). In both WT and ifnar−/− poly(I:C) stimulation results in increased IKK activity during the early phase. Following this WT cells undergo 50% translation inhibition and IKK activity decreases. ifnar−/− cells lack translation inhibition (horizontal dashed line, Figure 3), and have decreased late-phase IKK activity [vertical dashed line, this (A–F)].