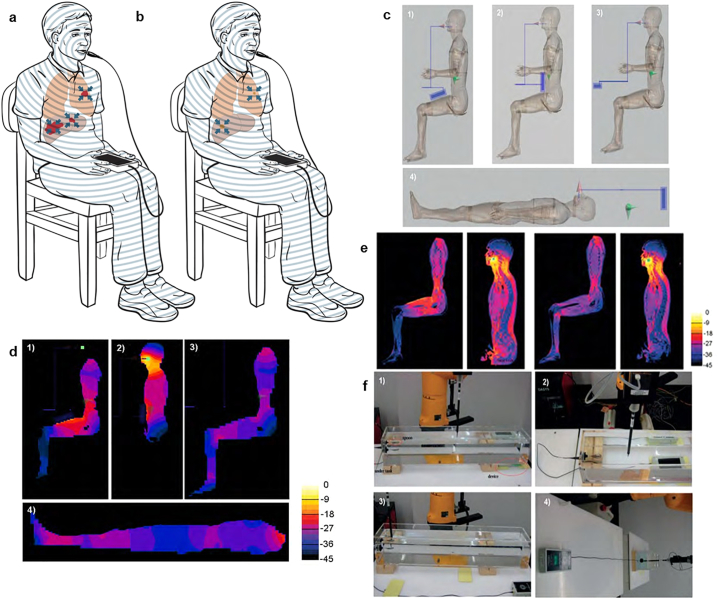
Fig. 1.
Intrabuccal delivery results in systemic absorption of AM RF EMF. a Patient with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving first treatment with the AM RF EMF emitting device. The concentric lines represent AM RF EMF emission from the spoon-shaped antenna placed on the patient's tongue. Red: primary and metastatic tumours. Blue arrows: depiction of antitumor activity location. b Same patient several months later with evidence of shrinkage or disappearance of the primary tumour and its metastases [10,11], Brown: shrunken tumour following AM RF EMF treatment, c,1) Patient sitting with device on thigh, 2) Patient sitting with device on the abdomen, 3) Patient sitting with device placed away from the body, 4) Patient in supine position to test the hypothesis that the body can act as one half of a short dipole antenna while the cable and device form the other half, or for treatment lying down while the device is behind the head. The device and coaxial cable are shown in blue. The electric dipole is shown in green. d, SAR slice views in the homogeneous human model: the images are normalized to 5 W/kg/W, with 3 dB/contour. 1) Patient sitting with device on thigh, 2) Patient sitting with device on the abdomen, 3) Patients sitting with device placed away from the body, 4) Patient in supine position. e, SAR slice views in the inhomogeneous model: the images are normalized to 5 W/kg/W, with 3 dB/contour. Left panels: patient sitting with device on thigh. Right panels: patient sitting with device located away from the body. f, Experimental validation measurements setups and results.1) The device is located at one extremity underneath the tank, 2) The device is in the middle underneath the tank, 3) The device is beside the tank, 4) The device is as far away from the tank as possible. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)