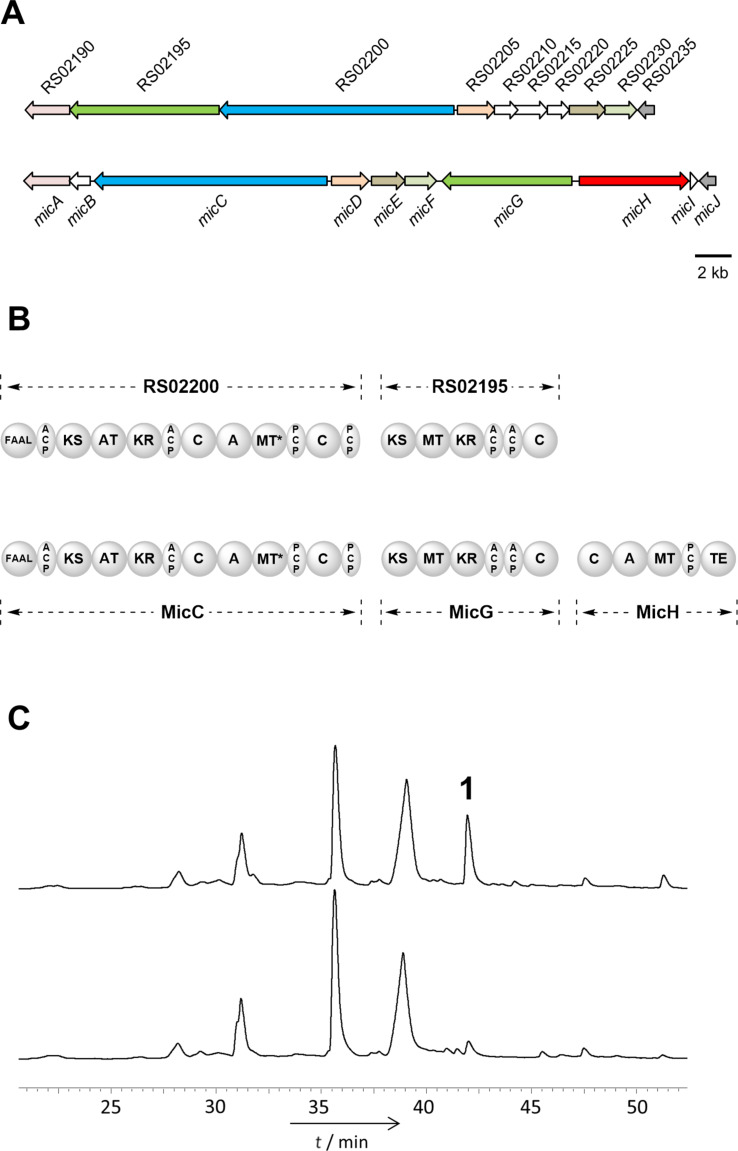
Figure 1.
A) Organization of the micacocidin-type gene cluster from Massilia sp. NR 4-1 (top) and of the mic gene cluster from R. solanacearum GMI1000 (bottom). The open reading frames are color-coded according to their predicted function. B) Domain architecture of the massiliachelin (top) and the micacocidin (bottom) assembly lines. Domain notation: FAAL, fatty acyl-AMP ligase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; KS, β-ketoacyl synthase; AT, acyltransferase; KR, ketoreductase; C, condensation; A, adenylation; MT, methyltransferase; PCP, peptidyl carrier protein; TE, thioesterase. The asterisk indicates a methyltransferase-like epimerization domain. C) UV chromatograms of crude culture extracts from Massilia sp. NR 4-1 grown under iron-deficient (top) and iron-replete (bottom) conditions. The chromatograms were recorded at a wavelength of 274 nm.