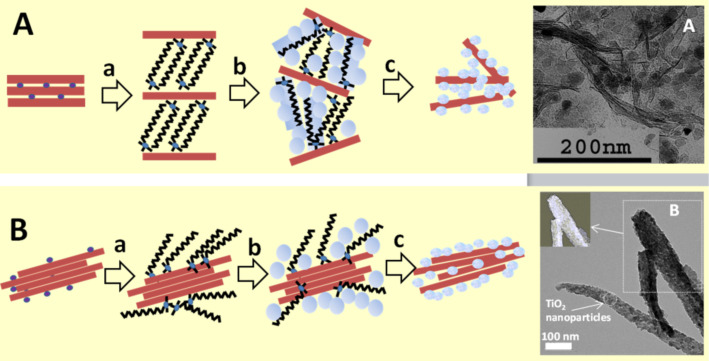
Figure 3.
Synthesis of clay–semiconductor nanoarchitectures by the “organoclay colloidal route” involving either smectites (A) or fibrous clays (B) in the following steps: a) replacement of inorganic cations by alkylammonium ions forming the intermediate organoclay, which is treated with metal-oxide precursors being transformed (b) into intermediate compounds that after calcination (c) finally yield the nanoarchitecture containing the photoactive semiconductor. TEM Images (on the right) of A: ZnO@smectite from Gafsa, where ZnO NPs were previously prepared from Zn acetate [118], and B: TEM of TiO2@sepiolite, where TiO2 NPs were prepared from titanium isopropoxide; reprinted with permission from [109], copyright 2008 American Chemical Society.