Figure 3.
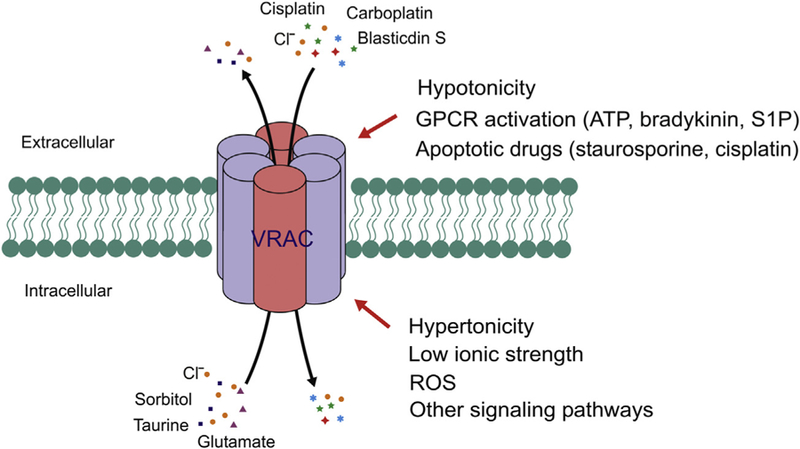
Diverse activation mechanisms and substrates suggesting an important role for VRAC in cell–cell communication. VRAC can be activated by extracellular hypertonicity, GPCR activation, and apoptosis-inducing drugs; and intracellular hypertonicity, reduced ionic strength, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). S1P, sphingosine-1-phos-phate. In addition to conducting Cl−, VRAC also permeate many organic osmolytes, metabolites, cancer drugs and antibiotics.
