Figure 4.
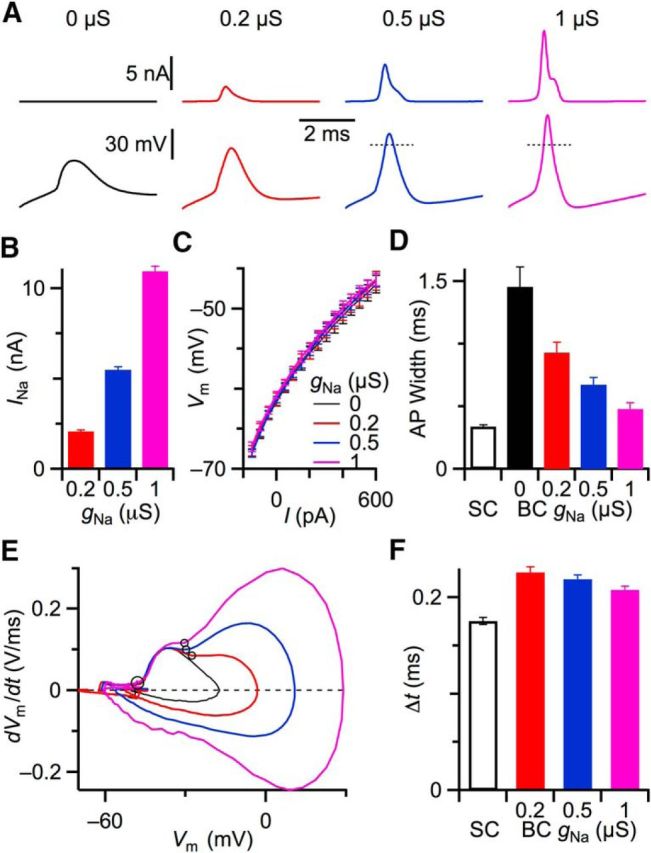
Adding a somatic Na conductance (gNa). using dynamic clamp. A, Effect of gNa on APs in a representative BC. APs were evoked by 600 pA current injection. Top traces represent Na current injected by dynamic clamp. Bottom traces represent APs. Short dashed lines indicate 0 mV. With increasing gNa, the BC fired faster, overshooting APs. B, Average peak amplitude of Na currents injected for different gNa (N = 10). C, Plots of average membrane potential as a function of current injection for BCs with different amounts of gNa. Adding gNa with dynamic clamp had no effect on BC input resistance (Rin for 0 μS = 40.8 ± 4.6 MΩ; Rin for 1 μS = 44.3 ± 3.8 MΩ; p = 0.4, N = 10). D, Average half-width of evoked AP in BC for different gNa (N = 31 cells). Half-width of SC AP is shown for comparison (N = 29 cells). E, Phase-plane plots of the example BC in A with different amounts of gNa. Circles represent the start of first and second phases. F, Time intervals between two phases of AP for SCs (N = 29) and BCs (N = 24) with different levels of gNa.
