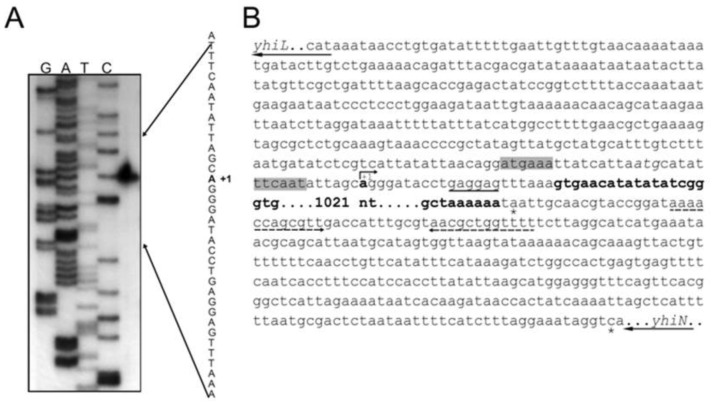
Figure 3. Sequence analysis and mapping of the yhiM transcriptional start site.
(A) Mapping of the 5′' end of the yhiM transcript by primer extension analysis. RNA was extracted from E. coli MC4100 stationary phase cells grown at pH 5.5 and reverse transcribed after priming with the oligonucleotide yhiM_revRT (Table 2), labelled at its 5′-end. Lanes G, A, T, and C are sequencing ladders of pCRIIyhiM with the same oligonucleotide used for the primer extension reaction. Sequencing reactions were run in parallel with the cDNA transcript (right lane). (B) Nucleotide sequence of the yhiL-yhiN genome region in E. coli MG1655. The bent arrow indicates the yhiM transcriptional start site at the residue in bold (+1). The sequences for the –10 and –35 putative promoter elements are on gray background. The potential Shine-Dalgarno sequence for ribosome binding is underlined. The yhiM ORF is in bold. The asterisks indicate the yhiM and yhiN stop codons. The dashed arrows indicate the inverted repeats probably generating a stem-loop like structure. The black arrows at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the sequence show the start and stop triplets as well as the direction of transcription of the yhiL and yhiN genes, respectively.