Figure 1.
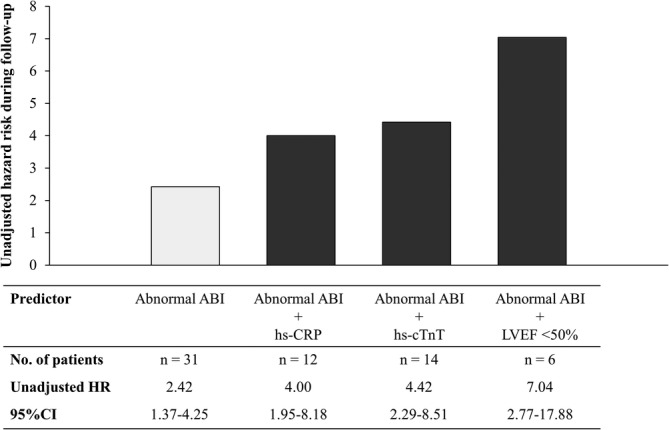
The figure shows hazard ratio and 95% confidence interval of abnormal ABI and combination of independent predictors of MACE obtained by univariate Cox regression analysis for the entire group (n = 104). Combination of predictors in addition to abnormal ABI (HR, 2.42; 95% CI 1.37‐4.25; P = .002) showed increased hazard ratio for abnormal ABI + upper tertile of hs‐CRP (HR, 4.00; 95% CI 1.95‐8.18; P < .001), abnormal ABI + upper tertile of hs‐cTnT (HR, 4.42; 95% CI 2.29‐8.51; P < .001), and abnormal ABI + LVEF <50% (HR, 7.04; 95% CI 2.77‐17.88; P < .001). The cutoff values for the upper tertile of hs‐TnT and hs‐CRP were 0.081 and 0.17 mg/dL, respectively. ABI, ankle‐brachial index; CI, confidence interval; CRP, C‐reactive protein; cTnT, cardiac troponin T; HR, hazard ratio; hs, high‐sensitive; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event
