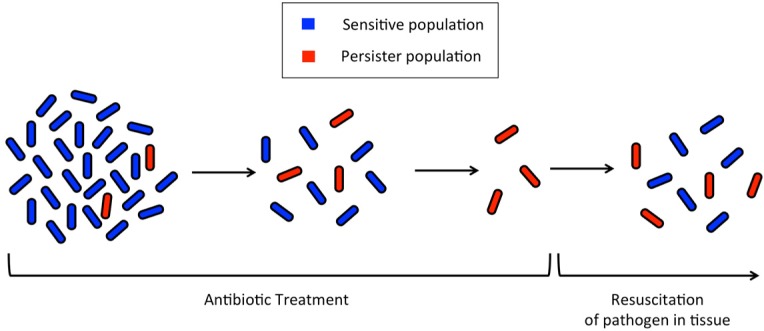
Figure 1. Progression of persister cell formation during antibiotic treatment.
At the onset of antibiotic exposure, the total cell population contains a small subset of persister cells that maintain a dormant but viable state. At the completion of the antibiotic regimen, susceptible cells are destroyed, but persister cells remain and are able to resuscitate, propagate a new population of cells, and cause recurrent disease.