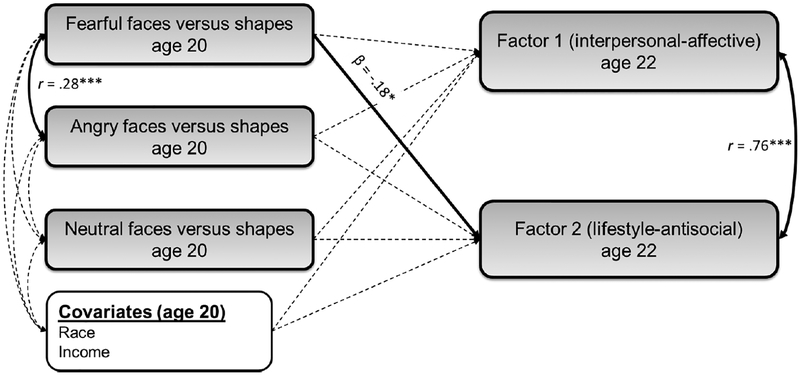
Figure 2.
Weakened negative amygdala-vmPFC functional connectivity during the processing of fearful faces versus shapes at age 20 is specifically related to Factor 2 psychopathy scores at age 22
Note. The processing of fearful faces < shapes (but not neutral faces < shapes or angry faces < shapes) at age 20 was significantly related to higher Factor 2 scores (i.e., irresponsible-lifestyle and antisocial behaviors) at age 22, accounting for race and income, as well as the covariance between predictors and outcomes within the model (see Supplemental Table 5, Model 1). Pathways that were modeled in the SEM, but that were non-significant, are shown as dotted grey lines. Model fit statistics: χ2=4.16, df=4, CFI=.999, TLI=.997, RMSEA=.02, SRMR=.03. Findings were unchanged when earlier antisocial behavior and callous-unemotional traits at age 20 were included as covariates in the model (Supplemental Table 5, Model 2). Notably, the difference in the path estimates from fearful faces versus shapes for Factor 1 and Factor 2 scores was not significantly different, based on calculating whether the confidence intervals overlapped by more or less than 50% (Cumming, 2009) (i.e., Δβ=.07, p>.05; see Supplemental Table 5).