Figure 3.
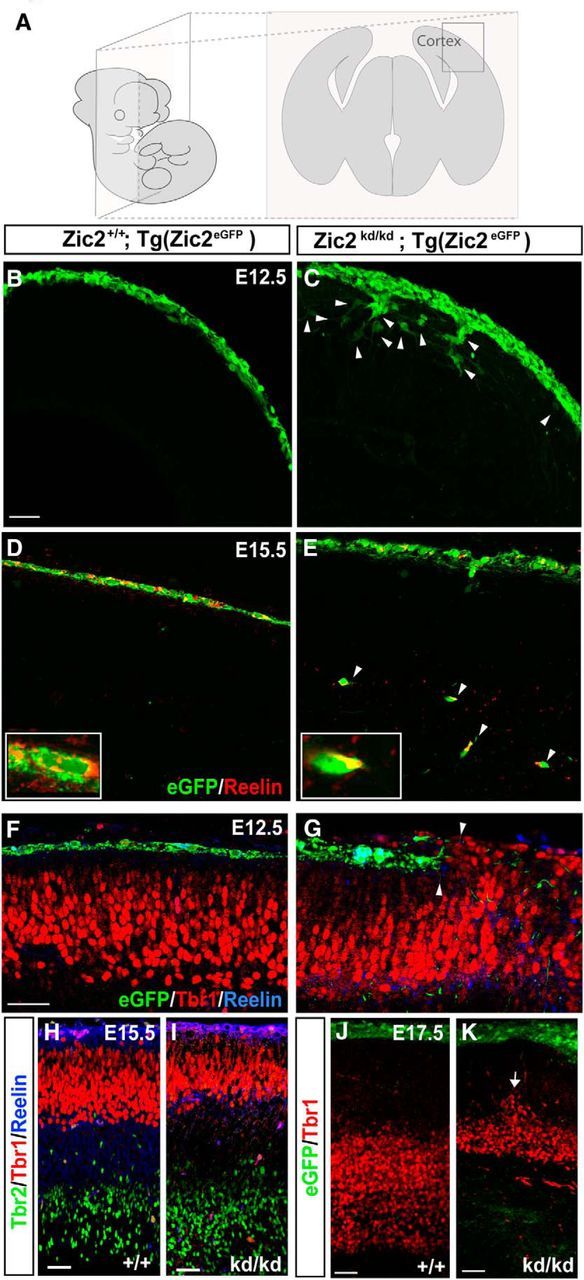
Zic2 mutants show cortical lamination defects. A, Schematic drawings representing the orientation and level of sectioning in the rest of the figure. B, C, Coronal sections of E12.5 Tg(Zic2eGFP) embryos showing that Zic2 CRCs are located in the superficial layer of the telencephalic vesicle, whereas in the Zic2 mutant embryos, eGFP cells were not restricted to the most superficial cortical layer. White arrowheads point to mislocated eGFP cells. D, E, Coronal sections of E15.5 Tg(Zic2eGFP) embryos showing that Zic2 CRCs are located in the telencephalic superficial layer. In contrast, in the Zic2 mutant embryos, many eGFP cells expressing reelin reached deep cortical laminae. White arrowheads point to mislocated eGFP/reelin cells. F–J, Inmunohistochemistry for Tbr1, Tbr2, and reelin in coronal sections of embryos at the indicated stages show that cortical layering, particularly the Tbr1 laminae, are affected from early stages of development (arrows) in the Zic2 mutant mice. Scale bars in B–K indicate 100 μm.
