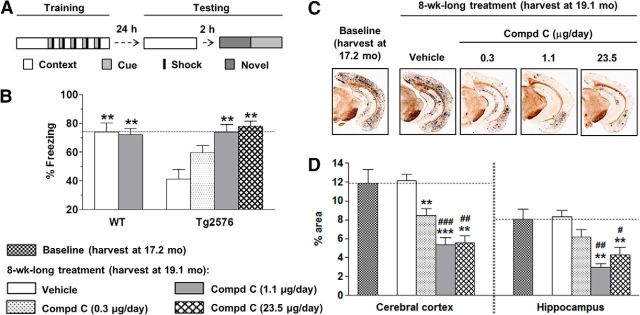
Figure 1.
Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion with BACE1 inhibitor, compound C, rescued behavioral deficit and reversed amyloid burden in aged Tg2576 mice. A, Fear-conditioning paradigm: mice were trained on day 1 in a specific context with a series of conditioning stimuli (tone cue followed by mild foot-shock). On day 2, freezing was evaluated in the same context (contextual fear memory), novel context (baseline), or cue alone (cued fear memory). B, Vehicle-treated Tg2576 mice show a deficit in contextual memory, compared with WT mice. A dose-dependent improvement in contextual fear memory was evident with intracerebroventricularly infused compound C. C, Low-magnification (×4) images illustrate amyloid plaques stained with Campbell–Switzer stain in cortex and hippocampus of Tg2576 mice at baseline and 8 weeks after intracerebroventricular infusion with vehicle or compound C. D, Percentage area occupied by amyloid plaques in vehicle-treated and compound C-treated mice. Significance versus vehicle-treated mice (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) and versus baseline (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001).