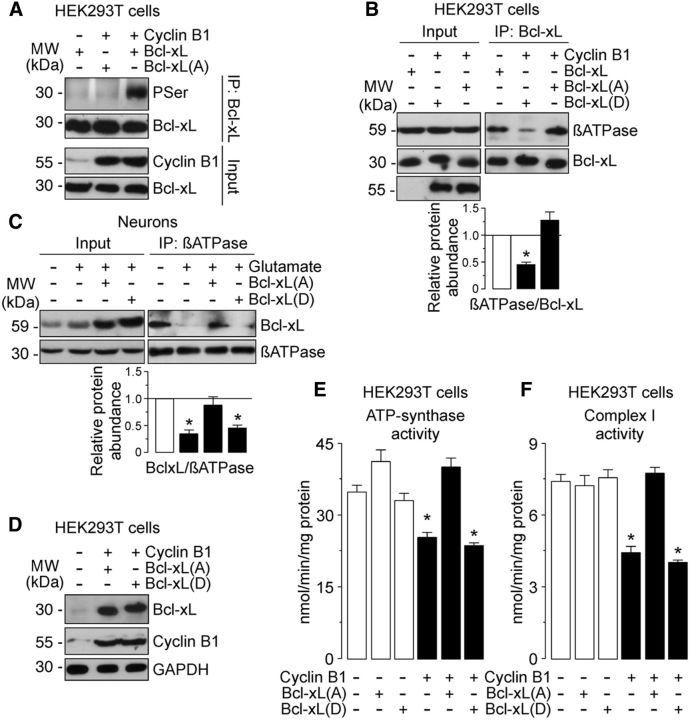
Figure 7.
Cyclin B1–Cdk1-induced Bcl-xL phosphorylation leading to its dissociation from β-F1Fo–ATP synthase causes ATP synthase and complex I inhibition on the excitotoxic stimulus. A, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with 0.8 μg/106 cells pIRES2–EGFP, either empty (Control) or containing the full-length cDNA of human cyclin B1, together with 0.8 μg/106 cells P8, either empty (Control) or containing the full-length cDNA of human Bcl-xL, the phosphodefective Bcl-xL(A) or the phosphomimetic Bcl-xL(D) Ser62–Bcl-xL mutants. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Bcl-xL antibody and analyzed by Western blot for phospho-Serine (PSer) and Bcl-xL. B, HEK293T cells were cotransfected as in B. Coimmunoprecipitation assay revealed that βATPase coprecipitated with Bcl-xL(A) but not with Bcl-xL(D). C, Neurons were transfected with 0.8 μg/106 cells P8, either empty or containing the full-length cDNA of human phosphodefective Bcl-xL(A) or phosphomimetic Bcl-xL(D) Ser62-Bcl-xL mutants. Neurons were then treated or not (−Glu) with 100 μm glutamate for 5 min and were further incubated in culture medium for 20 h. Coimmunoprecipitation assay reveals that the Bcl-xL(A), but not the Bcl-xL(D), mutant restored the interaction of Bcl-xL with the β-F1Fo–ATP synthase in neurons on the excitotoxic stimulus. In B and C, a representative Western blot is shown of three. Bar graphs represent the relative band intensity compared with −Cyclin B1 (B) or −Glu (C). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of three independent cell (B) or neuronal (C) cultures (n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus −Cyclin B1 (B) or − Glu (C). E, F, HEK293T cells were cotransfected as in B. The expression of Bcl-xL(A), but not Bcl-xL(D), fully prevented inhibition of ATP synthase (E) and complex I (F) activities in cyclin B1-expressing cells. *p < 0.05 versus −Cyclin B1. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent cell cultures (n = 3). MW, Molecular weight.