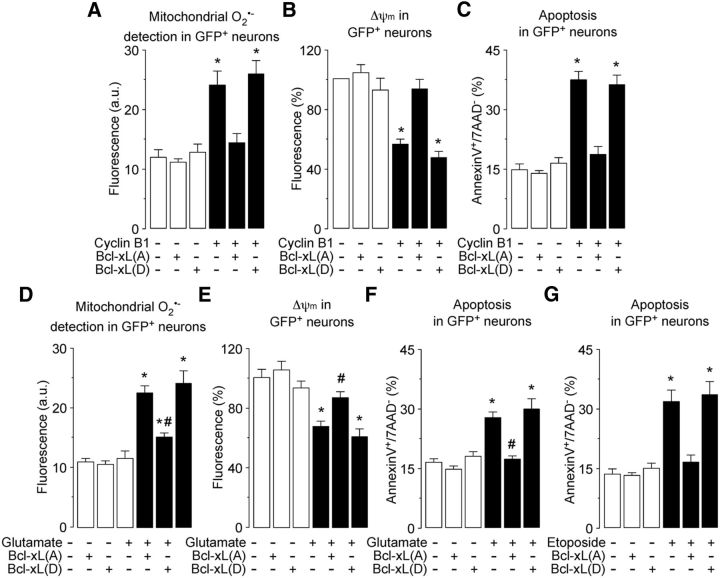
Figure 8.
Cyclin B1–Cdk1-induced Bcl-xL phosphorylation accounts for oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction on the excitotoxic stimulus. A–C, Neurons cells were cotransfected with 0.8 μg/106 cells pIRES2–EGFP, either empty (Control) or containing the full-length cDNA of human cyclin B1, together with 0.8 μg/106 cells P8, either empty (Control) or containing the full-length cDNA of human phosphodefective Bcl-xL(A) or phosphomimetic, Bcl-xL(D) Ser62-Bcl-xL mutants. Mitochondrial O2·− generation (A), mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) (B), and neuronal apoptotic death (annexin V+/7-AAD− neurons) (C) were assayed by flow cytometry in transfected (GFP+) neurons. The expression of Bcl-xL(A), but not Bcl-xL(D), prevented cyclin B1-induced oxidative stress (A), Δψm loss (B), and apoptosis (C) in neurons. *p < 0.05 versus −Cyclin B1 (control). D–F, Neurons were transfected with 0.8 μg/106 cells P8, either empty (control) or containing human phosphodefective Bcl-xL(A) or phosphomimetic Bcl-xL(D) Ser62–Bcl-xL mutants. Neurons were then treated or not (−Glu) with 100 μm glutamate for 5 min and were further incubated in culture medium for 20 h. The expression of Bcl-xL(A), but not Bcl-xL(D), prevented glutamate-induced oxidative stress (D), Δψm loss (E), and apoptosis (F) in neurons. *p < 0.05 versus −Glu (control); #p < 0.05 versus glutamate. G, Neurons were transfected as in D and then were exposed to etoposide (10 μm) for 24 h. The expression of Bcl-xL(A), but not Bcl-xL(D), prevented glutamate-induced neuronal apoptosis. *p < 0.05 versus −Etoposide (control). In all cases, data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three or four independent neuronal cultures (n = 3–4).