Figure 1.
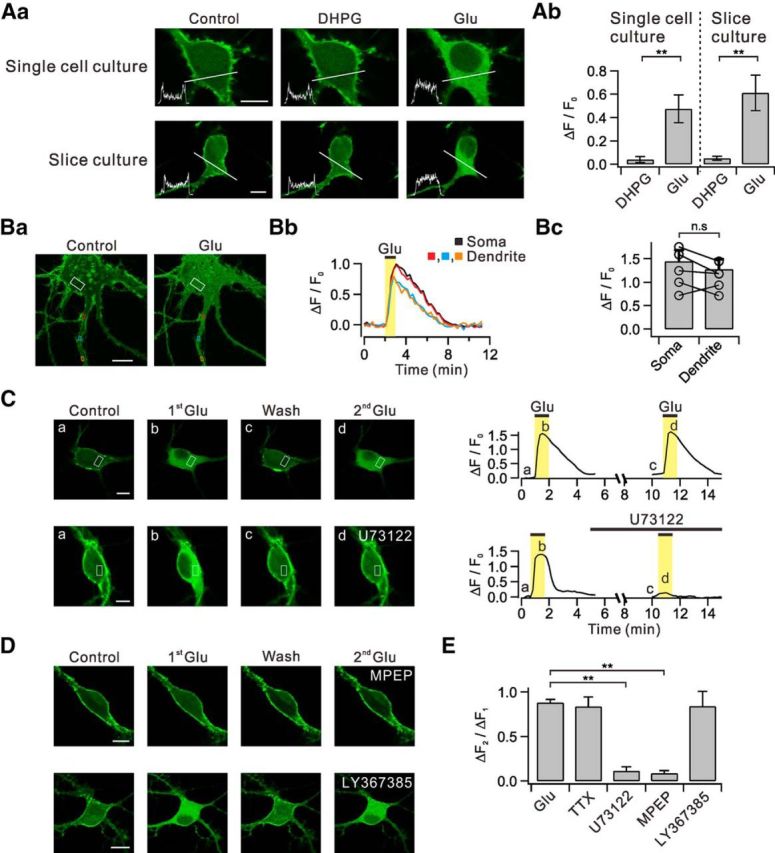
Glutamate, but not DHPG, induces translocation of PHδ-GFP via the mGluR5-PLC pathways. Aa, Dissociated hippocampal neurons in primary culture (single-cell culture) transfected with PHδ-GFP showed prominent green fluorescence signals in plasma membrane versus cytosol (Control). DHPG and glutamate (Glu) was applied to bath to see whether they induce PHδ-GFP translocation. Line profiles of fluorescence intensity (insets) were obtained across the white lines. Similar series of experiments were performed with hippocampal neurons in organotypic slice culture transfected with PHδ-GFP. Ab, Summary data showing the relative amplitudes of DHPG-induced and glutamate-induced PHδ-GFP translocation (ΔF/F0) in single-cell and slice culture conditions. Ba, Glutamate-induced PHδ-GFP translocation (ΔF/F0) was measured in ROIs of somatic cytosol (white) and multiple regions of dendritic cytosol (red, blue, and orange). Bb, Time courses of ΔF/F0 measured in designated ROIs. Bc, Bar graphs summarize the amplitudes of DHPG-induced or glutamate-induced PHδ-GFP translocation in soma and dendrites. C, Consecutive applications of 30 μm glutamate in control and in the presence of U73122. Images of PHδ-GFP-transfected neurons (left) and time courses of ΔF/F0 measured in designated ROIs (right). D, Effect of specific blockers for mGluR5 or mGluR1 on PHδ-GFP translocation. E, Bar graphs summarize ΔF2/ΔF1 in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and other experimental conditions described in C and D. n.s p > 0.05; **p < 0.01. Scale bar, 10 μm in all panels where indicated. Error bars represent SEM.
