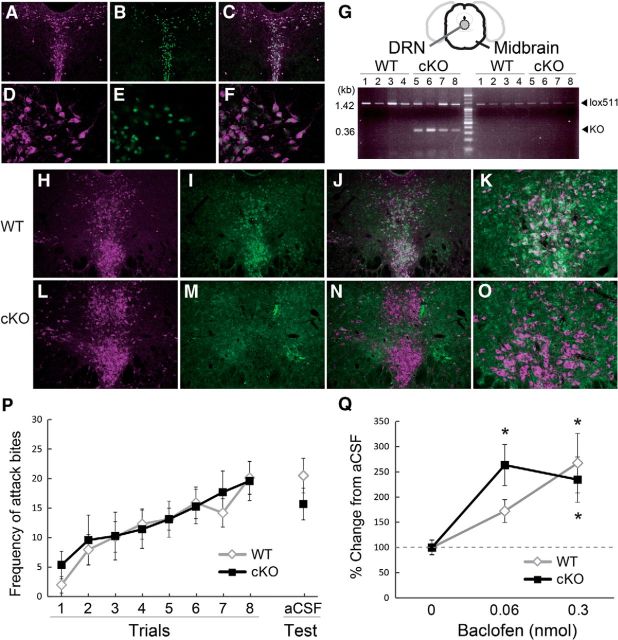
Figure 1.
Escalated aggression induced by intra-DRN baclofen in the conditional knock-out mouse of GABAB receptor on 5-HT neurons. 5-HTT-Cre mouse expresses Cre protein in Tph-positive 5-HT raphe neurons in the midbrain (A–F). Immunostaining of Tph (A, D; Sigma-Aldrich, anti-Tph 1:1000) and β-gal (B, E; Millipore, anti-β-gal 1:1000), and colocalization of Tph and β-gal (C, F) in the DRN of 5-HTT-Cre mice crossed with RNZ reporter mice with 10× (A–C) and 40× (D–F) magnification. G, PCR analysis showed that 5-HT neuron-specific GABAB receptor cKO mice (n = 4) possessed KO allele as well as floxed allele (lox511) in the DRN puncture, whereas only floxed allele was detected in midbrain leftover sample. WT mice (n = 4) showed only floxed allele in both DRN and midbrain sample. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the deletion of GABAB receptor expression on Tph-positive 5-HT neurons in cKO mice (L–O) in comparison with WT mice (H–K). Immunostaining of Tph (H, L) (Millipore, anti-Tph 1:500) and GABAB receptor (I, M; Abcam, anti-GABAB receptor 1, 1:300) and colocalization of Tph and GABA B receptor (J, K, N, O) with 10× (H–J, L–N) and 20× (K, O) magnification. P, Frequency of attack bites in cKO and its WT littermate did not differ before the surgery and at the vehicle injection into the DRN. Q, Effect of intra-DRN baclofen on attack bites behavior in cKO and WT littermate. Both cKO and WT littermate showed significant increase of attack bites by 0.3 nmol baclofen from its aCSF level, whereas 0.06 nmol baclofen significantly increased attack bites only in cKO mice. Data are mean ± SEM expressed as percentage change from vehicle; *p < 0.05 compared with its vehicle control within the genotype.