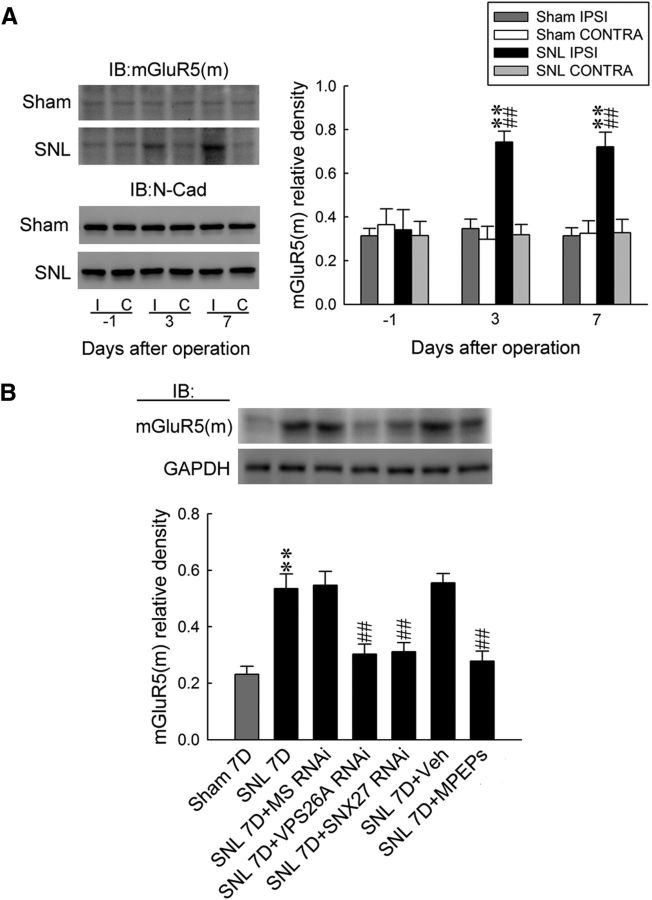
Figure 6.
The VPS26A–SNX27 complex drives mGluR5 membrane trafficking to mediate neuropathic pain in the dorsal horn. A, A representative Western blot and statistical analyses (normalized to N-Cad) showed that SNL, but not the sham operation (sham), increased the abundance of mGluR5(m) selectively in the ipsilateral (I and IPSI), but not contralateral (C and CONTRA), dorsal horn at days 3 and 7 after the operation. Statistical analyses included two-way ANOVA with repeated measures over time, group (F(3,20) = 28.47; p < 0.001) and time (F(2,40) = 2.595; p = 0.087) and in the interaction of group by time (F(6,40) = 3.281; p = 0.010), post hoc Tukey's tests. **p < 0.01 vs sham IPSI. ##p < 0.01 vs SNL day −1, n = 6. IB, Immunoblotting. B, Focal knock-down of spinal VPS26A and SNX27 expression using specific antisense siRNA (5 μg of SNL 7D+VPS26A RNAi and 3 μg of SNL 7D+SNX27 RNAi, 10 μl) and application of MPEPs (SNL 7D+MPEPs, 300 nm, 10 μl) all reversed the SNL-enhanced expression of membrane-bound mGluR5 on day 7 after the operation. One-way ANOVA, F(6,77) = 30.14, p < 0.001, post hoc Tukey's tests. **p < 0.01 vs sham 7D. ##p < 0.01 vs SNL 7D. n = 6.