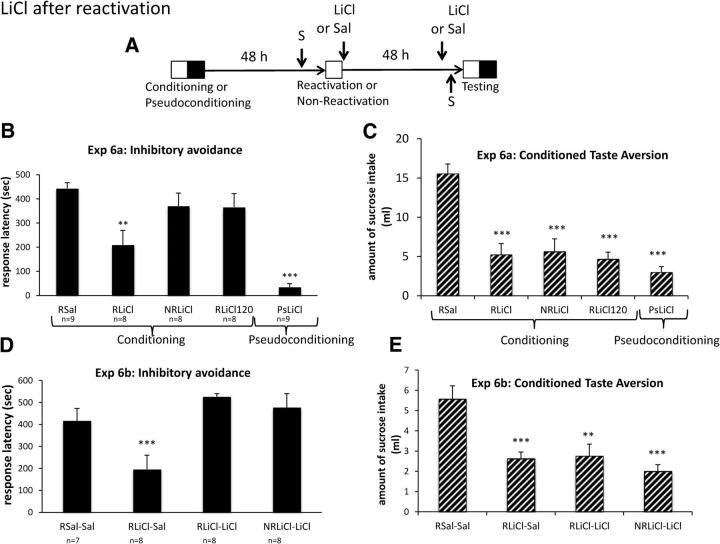
Figure 4.
LiCl after reactivation of memory induces CTA and inhibitory avoidance amnesia that is reversible with exposure to LiCl. A, Timeline of experiment. Reactivation or no reactivation took placed just after sucrose exposure, 48 h after conditioning or pseudoconditioning. All groups of rats (n = 7–9; B, C) received a Sal or LiCl (0.25 m; 300 mg/kg) injection delivered either just after the end of reactivation or 120 min later. The CTA occurred 48 h after memory reactivation. B, Experiment 6a, Values displayed as mean ± SEM response latency obtained during the test, 48 h after reactivation of inhibitory avoidance conditioning. C, Experiment 6a, Values displayed as mean ± SEM amount of sucrose intake obtained during the test for CTA. **p < 0.01 versus RSal; ***p < 0.001 versus RSal. D, Experiment 6b, In this experiment, rats received an additional injection of Sal or LiCl (0.15 m; 127 mg/kg), 30 min before the retention test. Values displayed mean ± SEM response latency obtained during the test, 48 h after reactivation of inhibitory avoidance conditioning. ***p < 0.001 versus RSal versus rSal–Sal. E, Experiment 6b, Values displayed as mean ± SEM amount of sucrose intake obtained during the CTA test. **p < 0.01 versus RSal–Sal; ***p < 0.001 versus RSal–Sal.