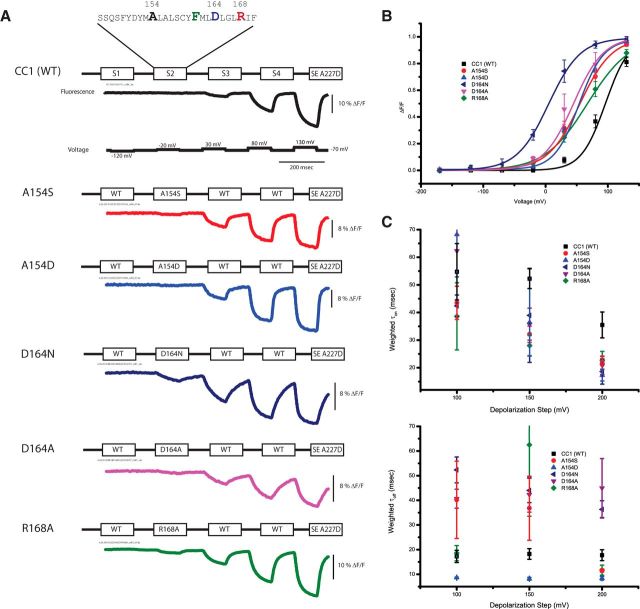
Figure 4.
Mutations in the S2 domain affect the speed and voltage sensitivity of the optical signal. A, Representative fluorescent traces of HEK293 cells expressing either the wild-type construct or an S2 mutant. The voltage protocol is the same for all constructs. The color coding is maintained for all panels. B, The optical signal was normalized and fitted to a Boltzman equation. All S2 mutations shifted the voltage response to more negative potentials. C, The weighted on and off taus of the optical signals for the 100, 150, and 200 mV depolarization steps. The optical signals were fitted to a single- or double-exponential decay. Because not all constructs were fit to a double exponential, the weighted taus (τ1 × % amplitude + τ2 × % amplitude) are plotted for comparison. The τon becomes faster as the depolarization strength increases, whereas τoff remains fairly constant over the different voltages. Error bars are SEM.