Figure 6.
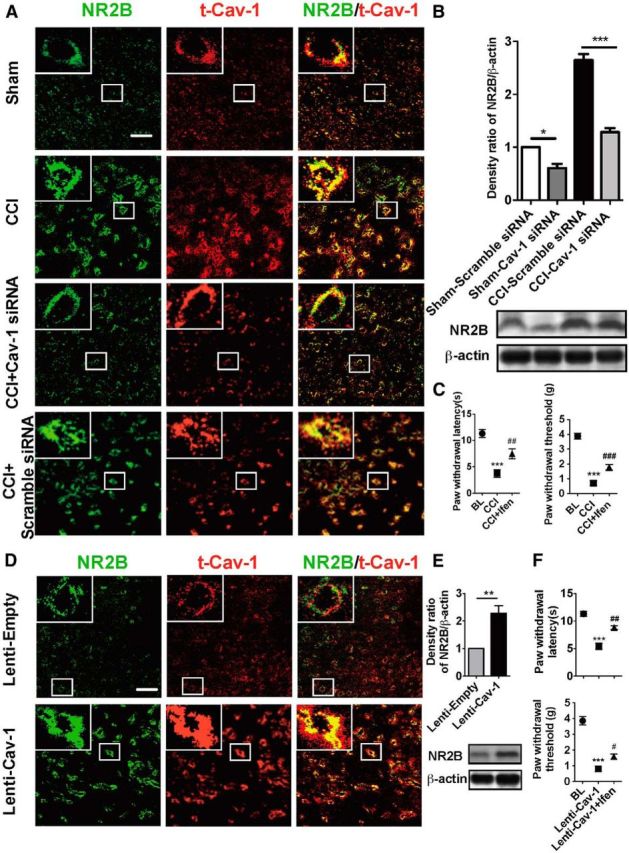
NR2B mediates pain modulation by Cav-1 in the ACC in CCI mice. A, Double immunofluorescence showed that Cav-1 colocalized with NMDA-NR2B in cell membrane in the ACC and CCI increased colocalization of Cav-1 and NMDA-NR2B. Knockdown of Cav-1 by intra-ACC injection of Cav-1 siRNA (10 μg/0.5 μl), but not by its control scramble siRNA, inhibited CCI-induced increase of colocalization of Cav-1 and NMDA-NR2B (n = 5). Scale bar, 50 μm. B, CCI increased the expression of NR2B in contralateral ACC, which could be reversed by knockdown of Cav-1 (n = 5). ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. C, Microinjection of NR2B inhibitor ifenprodil (0.5 μg/0.5 μl) into contralateral ACC significantly inhibited CCI-induced thermal hyperalgesia (left) and mechanical allodynia (right). Behavioral test was performed at 3 d before injury, 7 d after CCI, and 1 h after injection of ifenprodil (n = 8). ***p < 0.001, compared with baseline (BL), ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared with CCI. D, Overexpression of Cav-1 with Lenti-Cav-1 (0.5 × 106 TU/0.5 μl), not its control Lenti-empty, increased colocalization of Cav-1 and NR2B in membrane in ipsilateral ACC (n = 5). Scale bar, 50 μm. E, Overexpression of Cav-1 with Lenti-Cav-1 (0.5 × 106 TU/0.5 μl), not its control Lenti-empty, increased expression of NR2B in ipsilateral ACC (n = 5). **p < 0.01. F, NR2B inhibitor ifenprodil (0.5 μg/0.5 μl) reversed thermal hyperalgesia (top) and mechanical allodynia (bottom) in the unaffected hindpaw induced by overexpression of Cav-1 in ipsilateral ACC in CCI mice (n = 8). Behavioral test was performed at 3 d before CCI, 72 h after Lenti-Cav-1 injection, and 1 h after injection of ifenprodil (n = 8). ***p < 0.001, compared with BL, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, compared Lenti-Cav-1. Data are shown as means ± SEM. BL, baseline; Ifen, ifenprodil.
