Figure 9.
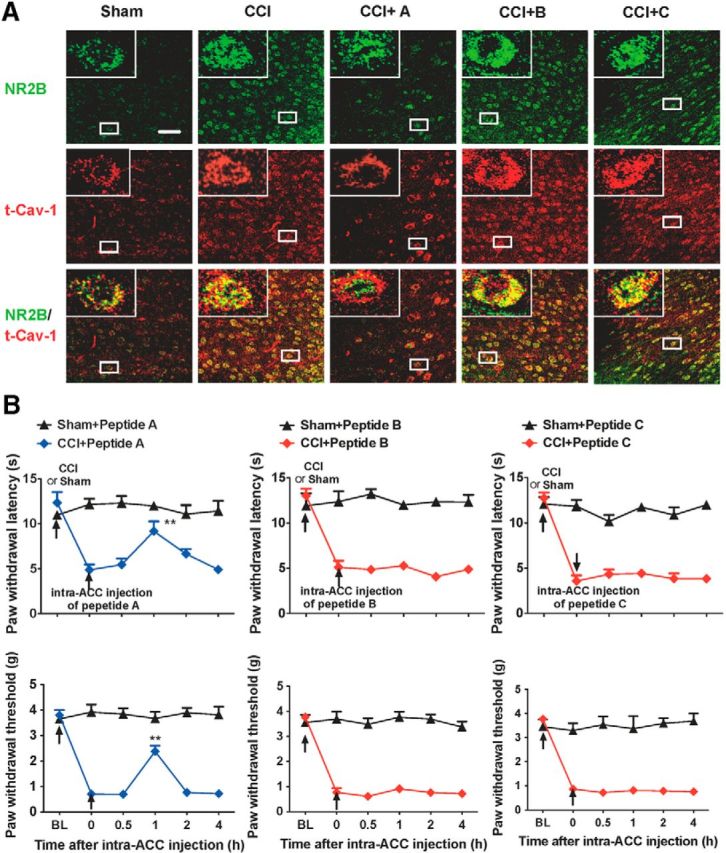
Disruption of the interaction of Cav-1 and NR2B in the ACC alleviates chronic neuropathic pain. A, Double immunofluorescence staining showed that intra-ACC injection of peptide A, not B and C, could inhibit CCI-induced increase of colocalization of t-Cav-1 and NR2B (n = 4). Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Intra-ACC injection of peptide A, not B or C, reversed CCI-induced thermal hyperalgesia (top) and mechanical allodynia (bottom). Behavioral test was performed at 3 d before CCI, 7 d after CCI, and 0.5–4 h after injection of peptides (n = 8). **p < 0.01, compared with 0 time point (before injection of peptides). Data are shown as means ± SEM. BL, baseline.
