Figure 2.
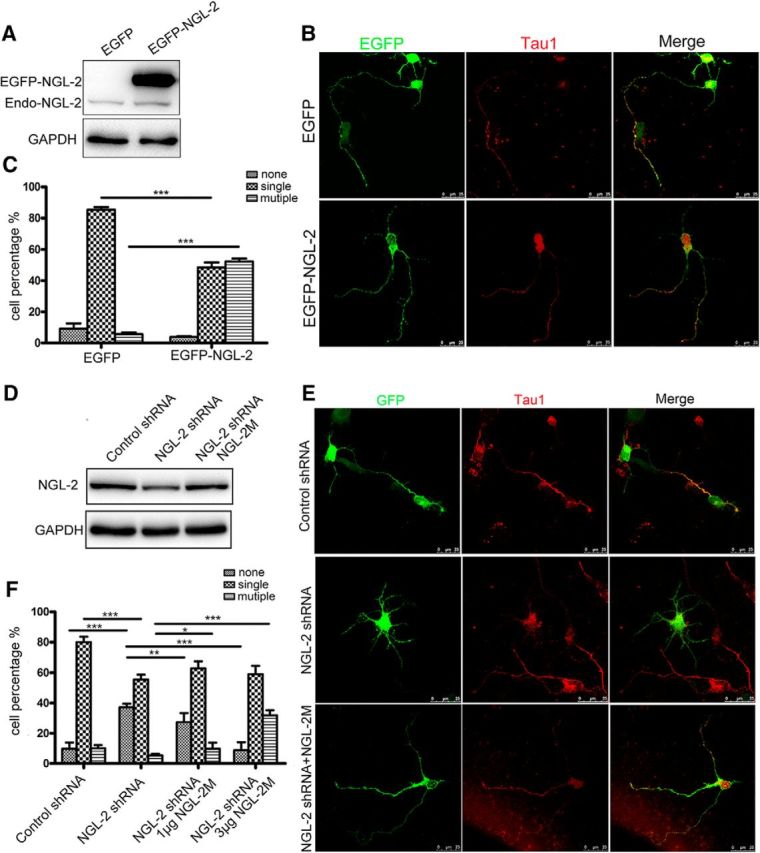
The effect of NGL-2 on axon differentiation. A, The transfection efficiency of NGL-2. Primary neurons were transfected with pEGFP-NGL-2 or pEGFP-empty vector. The level of NGL-2 was assessed by immunoblotting. B, Increase in axon numbers in neurons overexpressing NGL-2. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with pEGFP-NGL-2 or pEGFP-empty vector. Transfected neurons were identified by EGFP and stained with axonal marker Tau1. Scale bar, 25 μm. C, Quantitative analysis of axon differentiation transfected by NGL-2. Transfected neurons were classified into the following three groups: none, neurons with short neurites in similar length; single, neurons with one process that was positive for Tau1 staining, and >100 μm and at least twice as long as the second longest process; and multiple, neurons with two or more processes positive for Tau1 staining and >100 μm or twice as long as other neurites. The error bars represent the SD. ***p < 0.001, Student's t test. D, The efficiency of NGL-2 knockdown. Primary neurons were transfected with control shRNA, NGL-2 shRNA or cotransfected with an RNAi-resistant NGL-2M and NGL-2 shRNA. The level of NGL-2 was assessed by immunoblotting. E, The axon formation transfected by NGL-2 shRNA. Hippocampal neurons transfected with control shRNA, NGL-2 shRNA or cotransfected with NGL-2M and NGL-2 shRNA were identified by GFP and cultured for 72 h. Axons were identified by anti-Tau1 antibodies. Scale bar, 25 μm. F, Quantitative analysis of axon differentiation transfected by NGL-2 shRNA. The error bars represent the SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student's t test.
