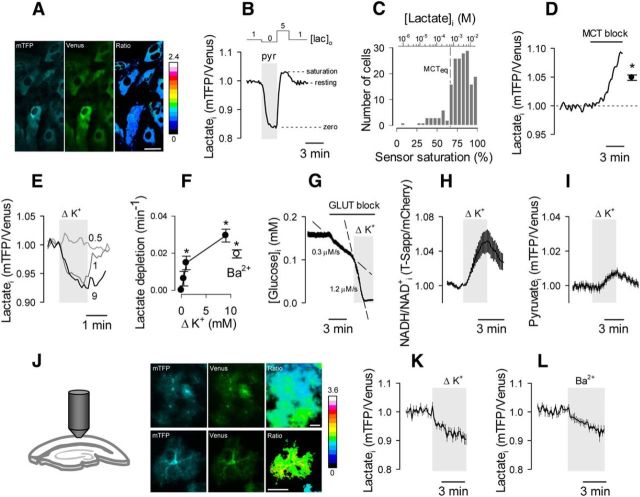
Figure 1.
Astrocytes maintain a cytosolic lactate reservoir that is depleted in the short term by high [K+]o. A, The FRET lactate sensor Laconic expressed in the cytosol of cultured astrocytes, showing mTFP (blue), Venus (green), and the ratio between mTFP and Venus. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Laconic was first depleted of lactate by superfusion with 10 mm pyruvate (pyr), and then saturated with 5 mm lactate and 2 mm glucose (San Martín et al., 2013). C, Resting lactate level in 183 cells (17 experiments), estimated with the protocol in B. The top x-axis indicates lactate concentration, according to the kinetic parameters estimated in vitro. Equilibrium concentration (MCTeq) of the monocarboxylate transporters. D, Response of intracellular lactate to 1 μm AR-C155858. The closed symbol represents the average change after 5 min of MCT blockage. E, Effect of 0.5, 1, and 9 mm [K+]o additions on the lactate level of an astrocyte. Resting [K+]o = 3 mm. F, Initial rates of K+-induced lactate depletion. The open symbol represents the initial rate of lactate depletion after exposure to 3 mm Ba2+. G–I, Effect of a 9 mm [K+]o rise on glucose consumption (G), cytosolic NADH/NAD+ ratio (H), and cytosolic pyruvate level (I). J, Protoplasmic astrocytes expressing Laconic observed in an acute cortical slice at low (top) and high (bottom) magnification. Scale bar, 20 μm. K, L, The effects of increasing [K+]o by 9 mm (K) or by adding 3 mm Ba2+ (L) on the lactate level of protoplasmic astrocytes are shown.