Figure 6.
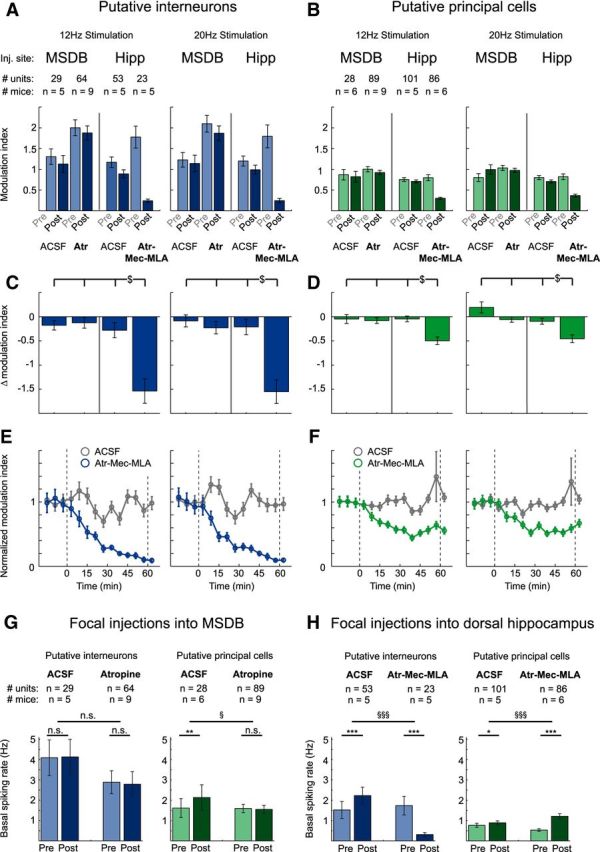
Modulation of neuronal activity in hippocampal area CA3 by cholinergic MSDB neurons is mediated via direct septo-hippocampal projections. A, B, Focal injections of atropine (Atr), 7.2 mm, into the MSDB had no effect, whereas focal injections of the cholinergic blocker mixture containing Atr, 7.2 mm, Mec, 10 mm, and MLA, 20 μm into the dorsal hippocampus strongly reduced stimulation-induced modulation of interneuron spiking rates (A) and principal cell firing rates (B). Data represent mean ± SEM of modulation indices of single units before and after focal injection of either ACSF or blocker into either the MSDB or the dorsal hippocampus (see A and B for number of analyzed units and mice). C, D, Difference between modulation indices of the post- and pre-conditions for every post versus pre pair shown in A and B. Frequency of light stimulation was 12 or 20 Hz as indicated ($p < 0.05 for difference between groups, two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer post hoc test). E, F, Onset of the effects of blocker injection into the hippocampus. Modulation index was determined as in A and B for 6 min time bins. The onset and offset of blocker injections are indicated with dashed lines. E, Interneurons. F, Principal neurons. Control experiments with ACSF injections are shown in gray, experiments with hippocampal blocker injections in blue or green, data are represented as mean ± SEM for the same neurons as in A–D. G, Focal injections of ACSF or Atr into the MSDB did not affect basal spiking rates of hippocampal putative interneurons (left). For putative principal cells (right), basal spiking rates were not affected by Atr and even slightly increased after ACSF injection. H, In contrast, focal injections of the cholinergic blocker mixture Atr-Mec-MLA strongly reduced basal spiking rates of putative interneurons (left), but strongly increased basal spiking rates of putative principal cells (right). ACSF injections only slightly increased basal spiking rates for both putative interneurons and principal cells. n.s., Not significant. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test for comparison between preapplication and postapplication conditions; § p < 0.05, §§§ p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U test for comparison between groups). See G and H for numbers of analyzed units and mice, 3–10 trials per condition and mouse.
