Figure 2.
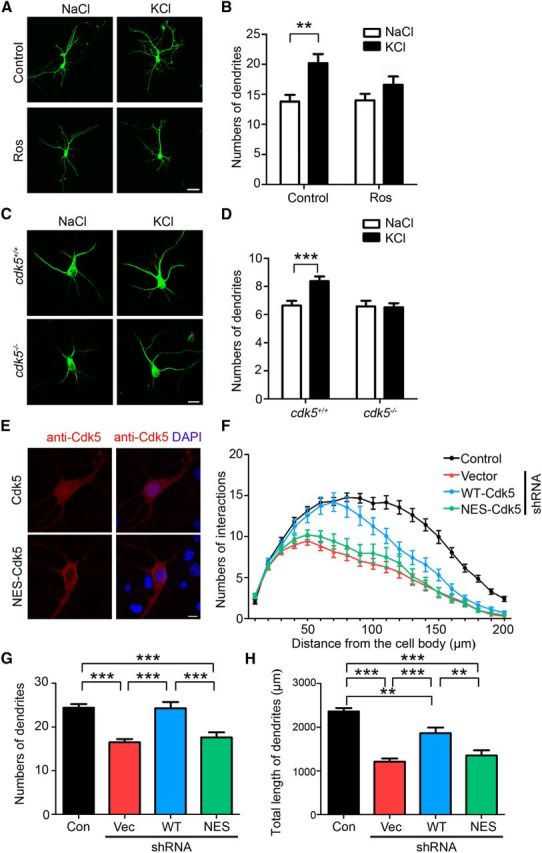
Cdk5 inhibition attenuates activity-dependent dendrite development. A, B, The increase in dendrite arborization after 24 h of KCl depolarization was attenuated by Ros. Cultured hippocampal neurons expressing GFP at 3 DIV were cotreated with 25 μm Ros. A, Representative images showing neuron morphology. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Quantification of dendrite number (mean ± SEM; n = 10; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, treatment × drug F(1,18) = 2.41, p = 0.1382, treatment F(1,18) = 1.93, p = 0.1821, drug F(1,18) = 11.48, p < 0.01, **p < 0.01). C, D, The KCl-induced dendritic growth was abolished in cdk5−/− neurons. C, Cultured hippocampal neurons from cdk5−/− mice and their littermates were treated with KCl and stained with dendritic marker MAP2 (green). Scale bar, 10 μm. D, Quantification of the dendrite (mean ± SEM; n = 6; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, treatment × genotype F(1,10) = 14.09, p < 0.001, treatment F(1,10) = 12.02, p < 0.01, genotype F(1,10) = 5.25, p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001). E–H, Cdk5 nuclear expression is important for dendrite development. E, Subcellular expressions of WT-Cdk5 and NES-Cdk5 in cultured hippocampal neurons. Cultured hippocampal neurons transfected with Cdk5 or its nuclear localization-deficient mutant (NES-Cdk5) were stained with Cdk5 antibody. Scale bar, 10 μm. F–H, Hippocampal neurons (7 DIV) were transfected with Cdk5 shRNA together with RNAi-resistant Cdk5 constructs. F, Sholl analysis of transfected neurons with Cdk5 shRNA and Cdk5 constructs. G, H, Knock-down of Cdk5 expression significantly reduced dendrite number and length. Coexpression of wild-type Cdk5 but not NES-Cdk5 rescued the defective dendritic arborization (mean ± SEM; n = 30 from three experiments; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
