Figure 4.
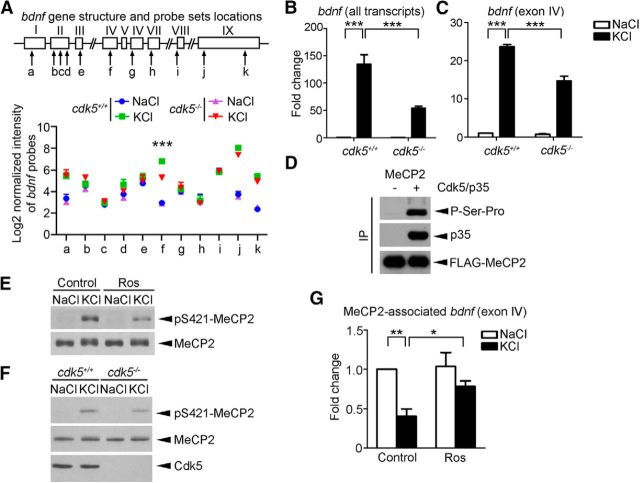
Cdk5 regulates MeCP2 phosphorylation and DNA-binding activity. A, Schematic diagram of mouse bdnf; exons and introns are represented by boxes and lines, respectively. The probes used are denoted as a–k. The log2 values of the normalized intensity of individual probe set are plotted (mean ± SEM from three independent experiments; ***p < 0.005, cdk5−/− vs cdk5+/+ in the KCl condition, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). B, C, Fold changes of all bdnf transcripts and activity-induced exon IV transcript in cdk5+/+ and cdk5−/− cortical neurons triggered by membrane depolarization determined by quantitative real-time PCR (mean ± SEM; n = 3; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, ***p < 0.001). Cortical neurons (10 DIV) derived from cdk5+/+ and cdk5−/− mice were treated with 50 mm KCl or NaCl for 6 h to examine bdnf mRNA expression. D, MeCP2 was phosphorylated by Cdk5/p35 at Ser-Pro site(s) in HEK293T cells. FLAG-tagged MeCP2 was immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG antibody, followed by Western blotting with antibody against proline-directed phosphoserine antibody. E, F, Regulation of KCl-induced Ser421 MeCP2 phosphorylation by Cdk5. E, Cultured cortical neurons were pretreated with 25 μm DMSO control or Ros for 1 h, followed by 50 mm KCl or NaCl for 30 min. The experiment was repeated at least three times. F, KCl-induced Ser421 MeCP2 phosphorylation was attenuated in cdk5−/− neurons. G, ChIP assay of MeCP2 followed by real-time PCR using bdnf exon IV promoter-specific primers (data were normalized to those of the Control+NaCl group; mean ± SEM; n = 5; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Cultured cortical neurons were pretreated with 25 μm DMSO control or Ros for 1 h, followed by 50 mm KCl or NaCl for 90 min.