Figure 6.
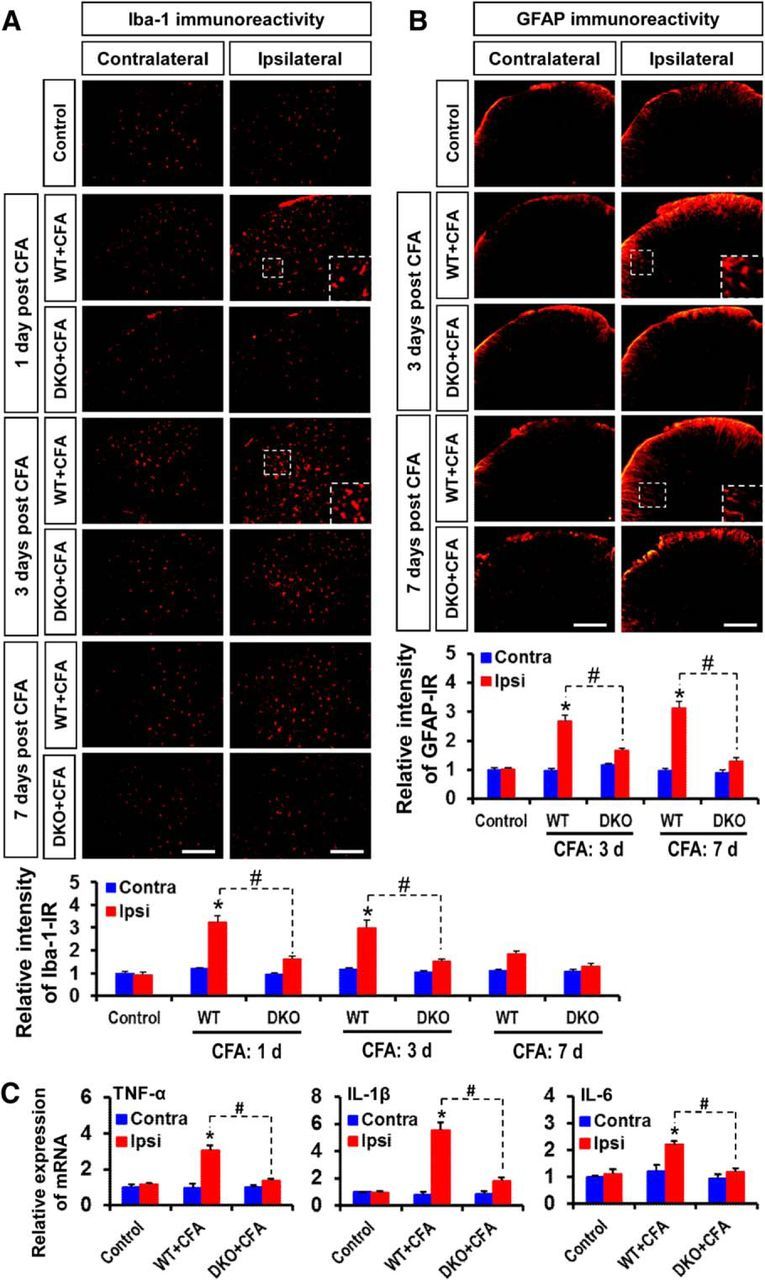
Role of PDK2/4 in glial activation and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord after intraplantar administration of CFA. A, Iba-1 (red, a microglia marker) immunoreactivity was significantly increased in the ipsilateral, but not in the contralateral, dorsal horn of the lumbar segment of the spinal cord at 1–3 d. The increased Iba-1 immunoreactivity persisted at a low level for 7 d after CFA injection. However, CFA-induced Iba-1 immunoreactivities were markedly attenuated in the Pdk2/4 DKO mice at all the time points. B, GFAP (red, an astrocyte marker) immunoreactivity was significantly increased in the ipsilateral, but not in the contralateral, dorsal horn of the lumbar segment of the spinal cord at 3–7 d after CFA injection. The CFA-induced GFAP immunoreactivities were markedly attenuated in the Pdk2/4 DKO mice at these time points. Insets, Magnified images (original magnification × 200). Quantifications and statistical analyses of stained images are presented in adjacent graphs. C, The relative mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the lumbar segment of the spinal cord at 3 d after injection was evaluated by real-time RT-PCR. Results for mRNA expression are displayed as the fold increase of gene expression normalized to GAPDH. *p < 0.05 versus the vehicle-treated control animals. #p < 0.05 between indicated groups (Student's t test). n = 3. Data are mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 200 μm. Images show the representative results of at least three independent experiments.
