Figure 8.
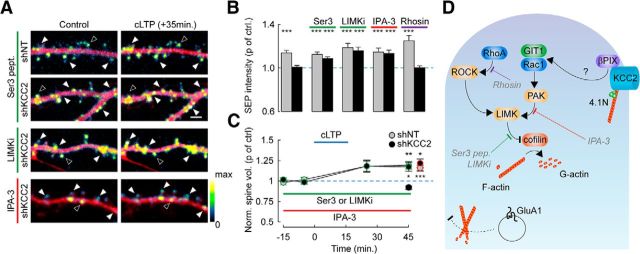
KCC2 controls actin depolymerization through a Rac1-PAK-LIMK pathway. A, Overlay of mCherry (red) and SEP (pseudocolors) spinning-disc fluorescence micrographs of dendritic sections of shNT or shKCC2-expressing neurons before (Control) and 35 min after cLTP induction. Neuron cultures were exposed either for 4 h to cofilin N-ter hexadeca-peptide fused to penetratin (Ser3 pept., 20 μg/ml) or the LIMK inhibitor LIMKi (10 μm), or for 24 h to the PAK inhibitor IPA-3 (5 μm). Filled arrowheads indicate cLTP-induced SEP fluorescence spots. Open arrowheads indicate spines with unchanged or reduced SEP fluorescence. Scale bar, 2 μm. B, Summary graph of SEP fluorescence as in A measured 35 min after cLTP induction and normalized to control, in neurons expressing SEP-GluA1 and either shNT or shKCC2 exposed to Ser3 peptide, LIMKi, IPA-3, or the RhoA inhibitor Rhosin (30 μm). ***p < 0.005. n = 7–29 neurons from the same cultures in each condition. C, Summary graph of average spine volume (normalized to control before cLTP induction) measured 30 min after cLTP induction, from the same experiments as above, either in control neurons (shKCC2; black symbols) or after 4 h exposure to LIMK inhibitors (Ser 3 peptide or LIMKi; green symbols) or 24 h exposure to IPA-3 (red symbols). *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.005. D, Scheme representing how cofilin plays a central role in regulating actin dynamics as it catalyzes depolymerization of F-actin into G-actin. Cofilin activity is inhibited by phosphorylation of its Ser3 residue by LIMK. Several signaling cascades converge to activate LIMK in neurons. These include the RhoA/ROCK as well as the Rac1/PAK pathways. βPIX, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) involved in Rac1 activation, has been shown to interact with KCC2 (Fig. 7D,E) (Llano et al., 2015). We propose that this interaction may hinder recruitment of βPIX and its scaffolding molecule GIT1 and, consequently, activation of Rac1/PAK at rest. Disrupting this interaction may then favor Rac1/PAK activation, increase LIMK activity, and thereby inactivate cofilin through Ser3 phosphorylation, resulting in enhanced actin polymerization. This in turn prevents LTP-induced membrane traffic of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors and increase in spine volume. The LIMK inhibitor LIMKi as well as the dominant-negative peptide Ser 3 pept. (gray) both favor actin depolymerization by antagonizing LIMK-mediated cofilin phosphorylation. The PAK inhibitor IPA-3 acts upstream to inhibit Rac1-mediated activation of LIMK. Rhosin specifically inhibits RhoA. In this scheme: orange represents kinases; blue represents Rho GTPases; purple represents GEF. Adapted from Cingolani and Goda (2008).